英国Kirkstall Quasi Vivo细胞灌流培养系统,Quasi Vivo Flow System
产品技术原理与优势
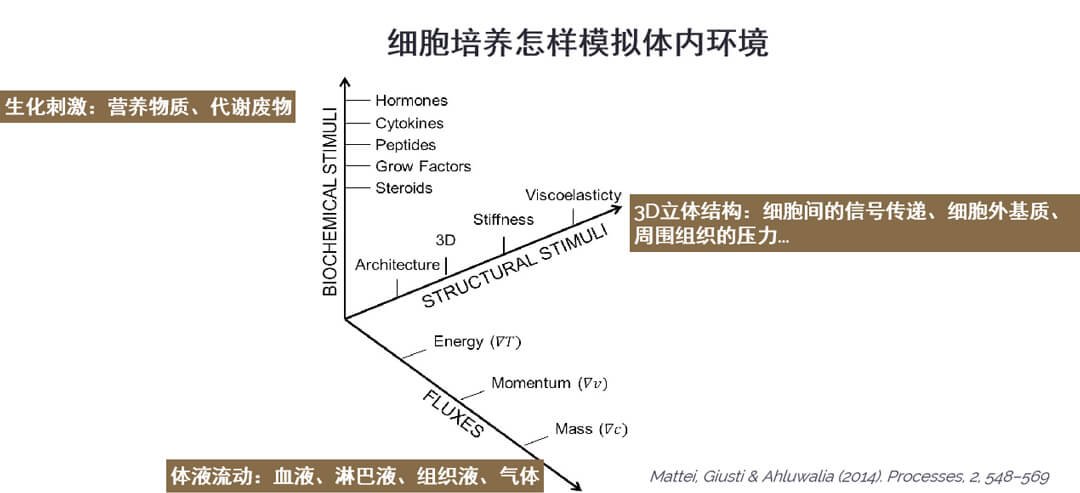
细胞培养基可以提供细胞生长所需的营养物质并稀释代谢废物。3D细胞培养可以提供立体结构。但是体液流动怎样模拟?来自英国Kirkstall公司的Quasi Vivo产品为此提供了解决方案。设计新颖的培养小室、高精度的低速蠕动泵结合到一起,实现了对体液流动的模拟。
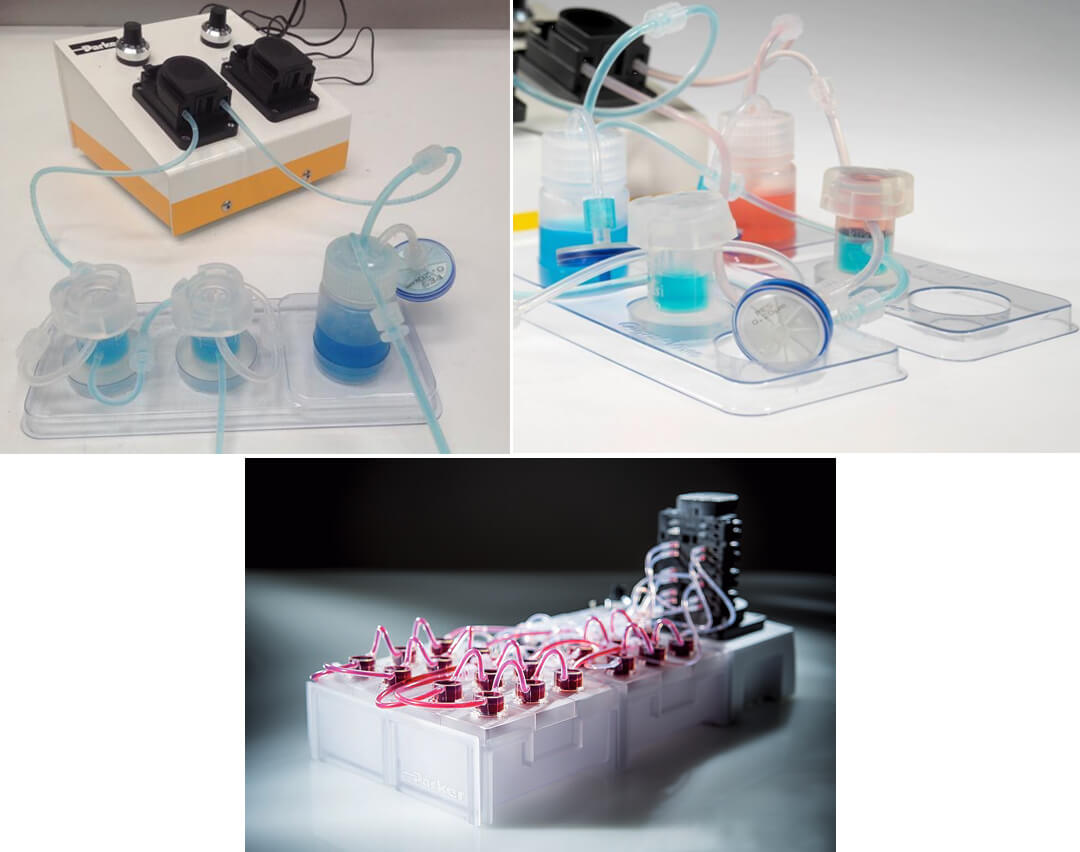

产品名称、货号、图片
| 货号 | 中文名 | 英文名 | 包装清单 | 单位 | 规格 |
| QV500SK | Quasi Vivo灌流培养系统QV500入门套装 | Quasi Vivo® QV500 Starter Kit | 3个QV500腔室,1个储液瓶,3个托架,管路和鲁尔接口,玻片与操作手册 | 盒 | 1套/盒 |
| QV600SK-ALI | Quasi Vivo灌流培养系统QV600入门套装-气液界面培养 | Quasi Vivo® QV600 Starter Kit Air Liquid Intece | 3个QV600腔室,1个储液瓶,3个托架,管路、鲁尔接口和操作手册 | 盒 | 1套/盒 |
| QV600SK-LLI | Quasi Vivo灌流培养系统QV600入门套装-液液界面培养 | Quasi Vivo® QV600 Starter Kit Liquid Liquid Intece | 3个QV600腔室,2个储液瓶,O形密封圈,3个托架,管路和鲁尔接口,备用滤器与操作手册 | 盒 | 1套/盒 |
| QV900SK | Quasi Vivo灌流培养系统QV900入门套装 | Quasi Vivo® QV900 Starter Kit | 3个QV900腔室,2个储液瓶,2个托架,管路、鲁尔接口和操作手册 | 盒 | 1套/盒 |
| QVPF22X0103 | 2通道低速蠕动泵 | Parker Polyflex 2-Channel Peristaltic Pump | 2通道低速蠕动泵 | 盒 | 1台/盒 |
| QV PF600 | 6通道低速蠕动泵 | Parker Polyflex 6-Channel Peristaltic Pump | 6通道低速蠕动泵 | 盒 | 1台/盒 |
| 备注:至少购买一个入门套装和一台低速蠕动泵才能开始实验! | |||||
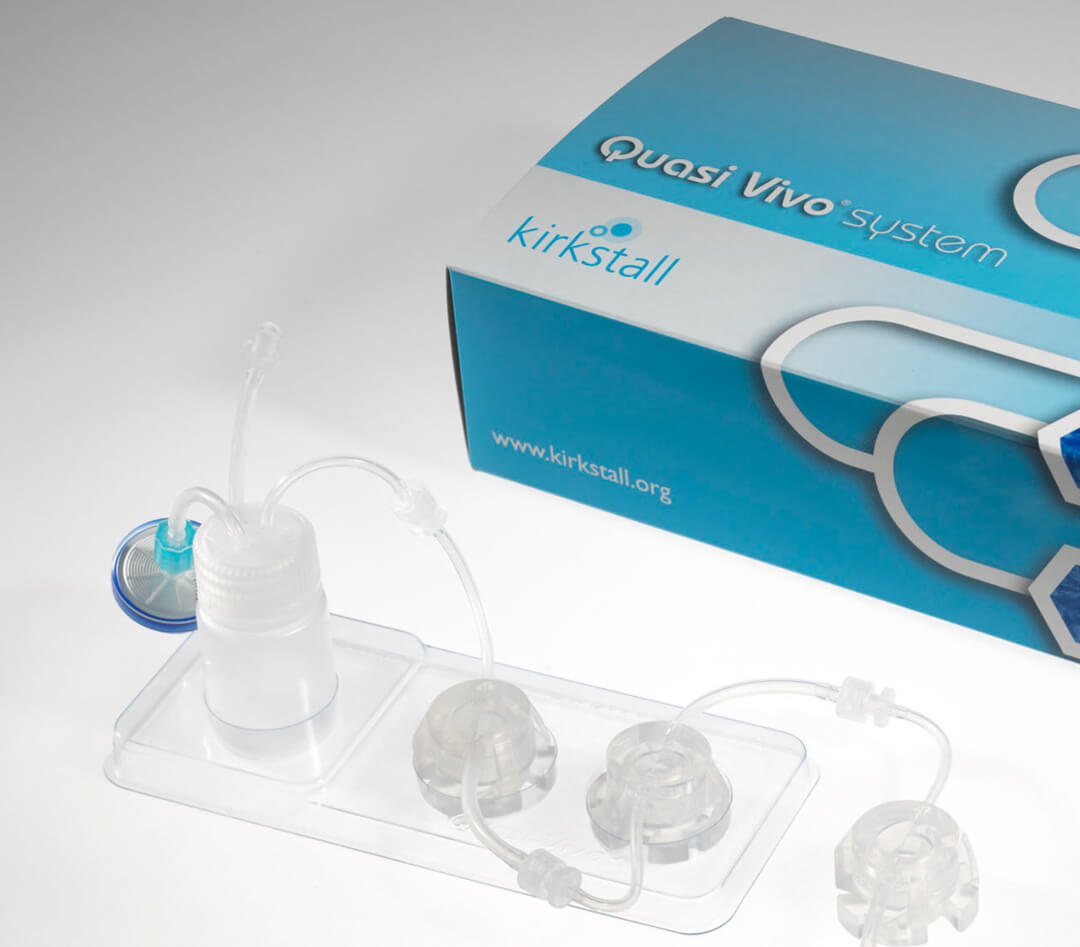
图1、QV500
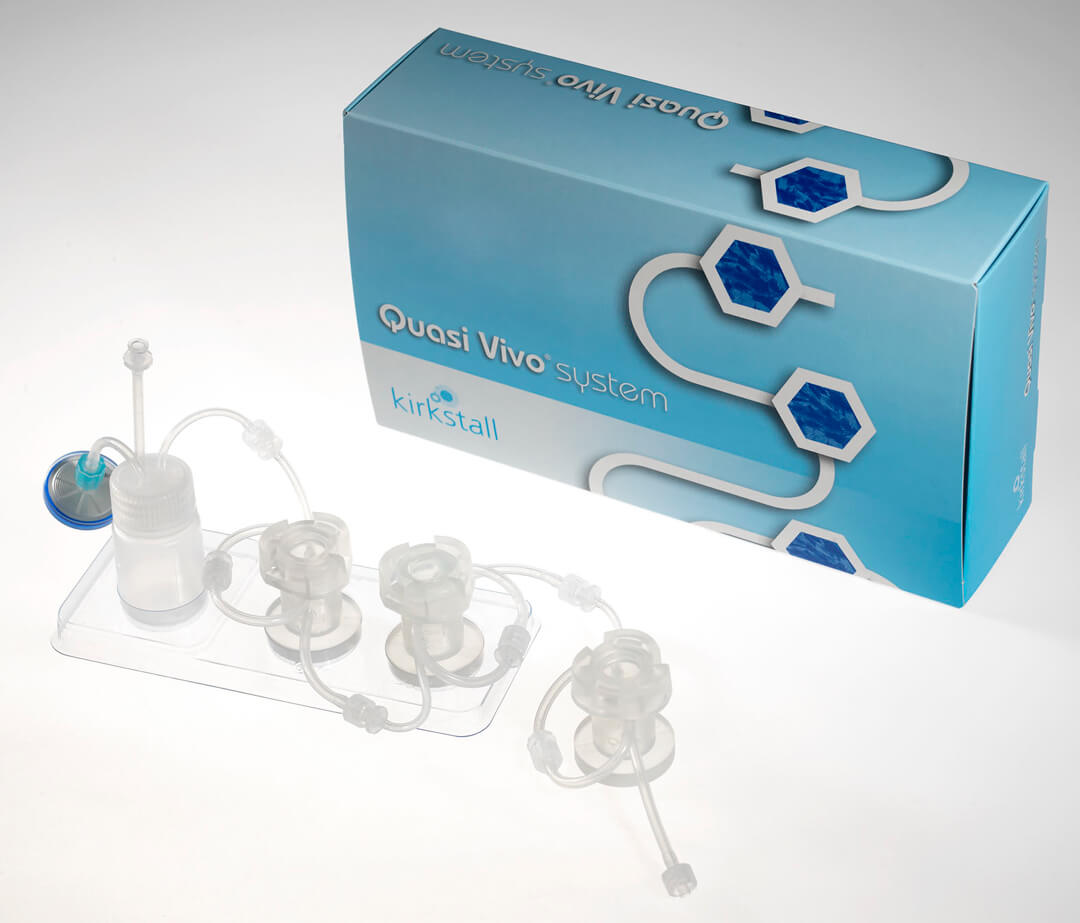
图2、QV600
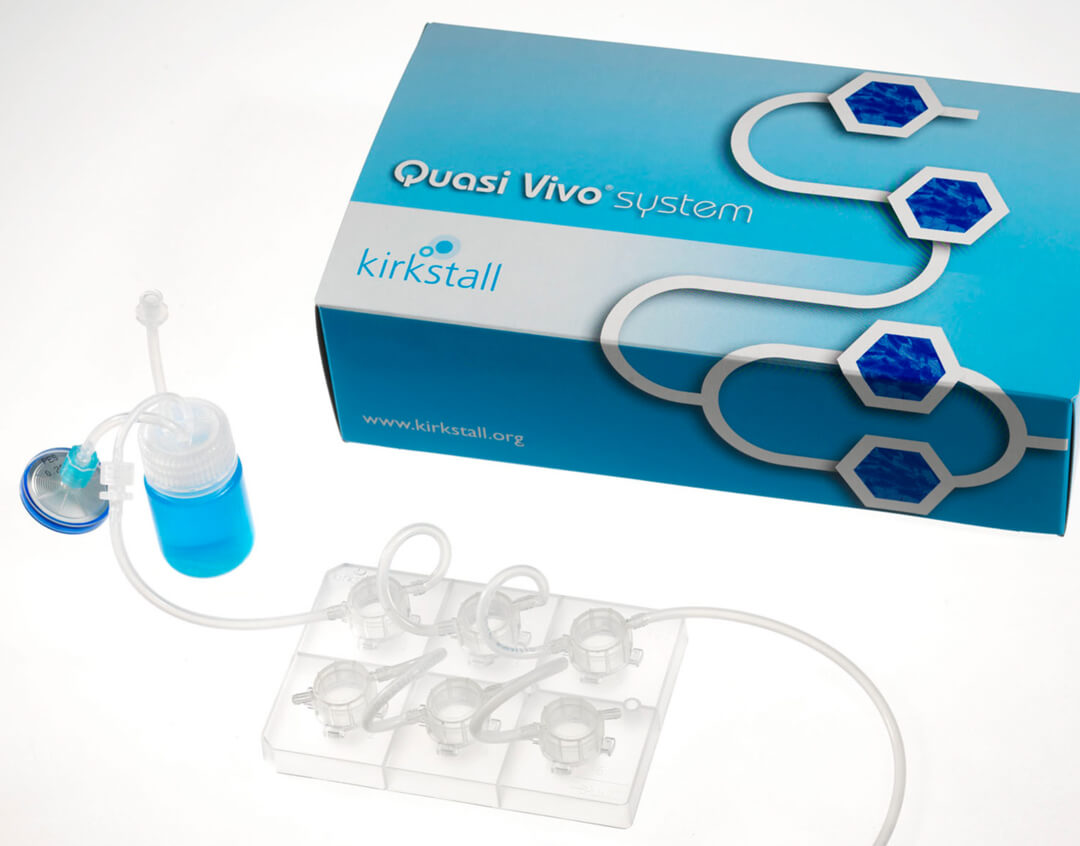
图3、QV900
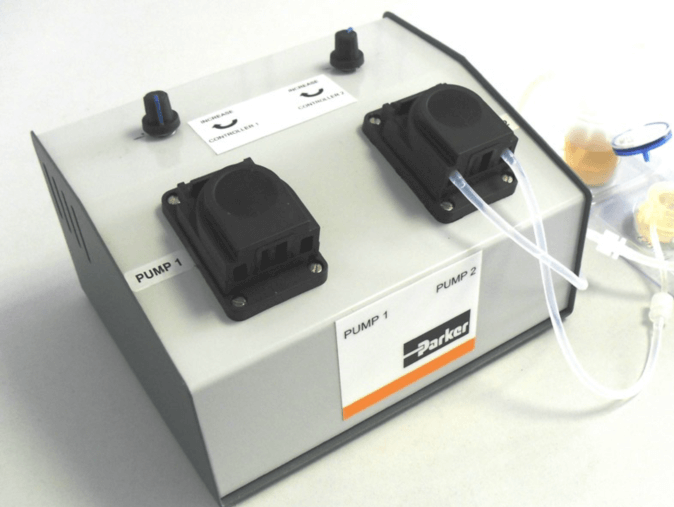
图4、2通道低速蠕动泵

图5、6通道低速蠕动泵
常见的培养方式举例
①单向流动培养 vs 循环流动培养
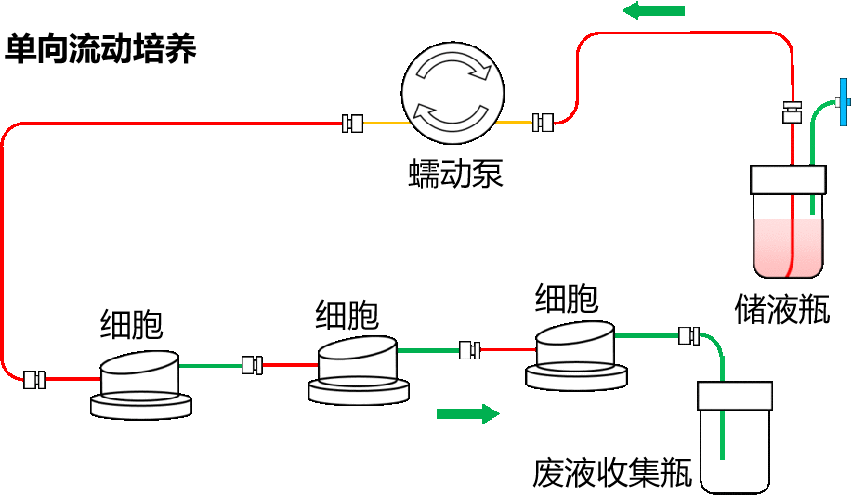
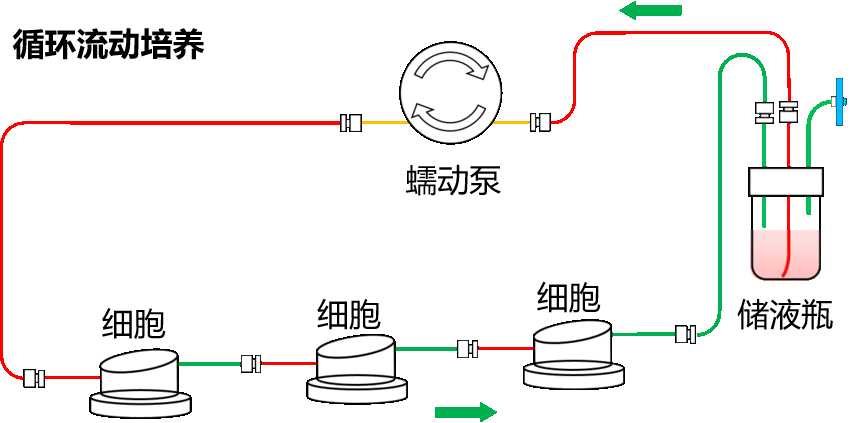
②培养一种细胞,培养基流动,让细胞获得更充足的氧气和营养物质
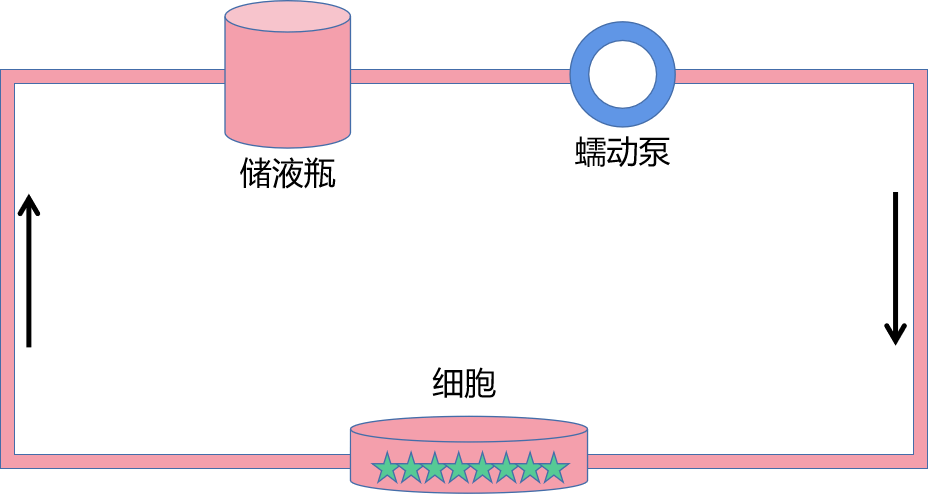
③多种细胞混合共培养,培养基流动,让细胞获得更充足的氧气和营养物质
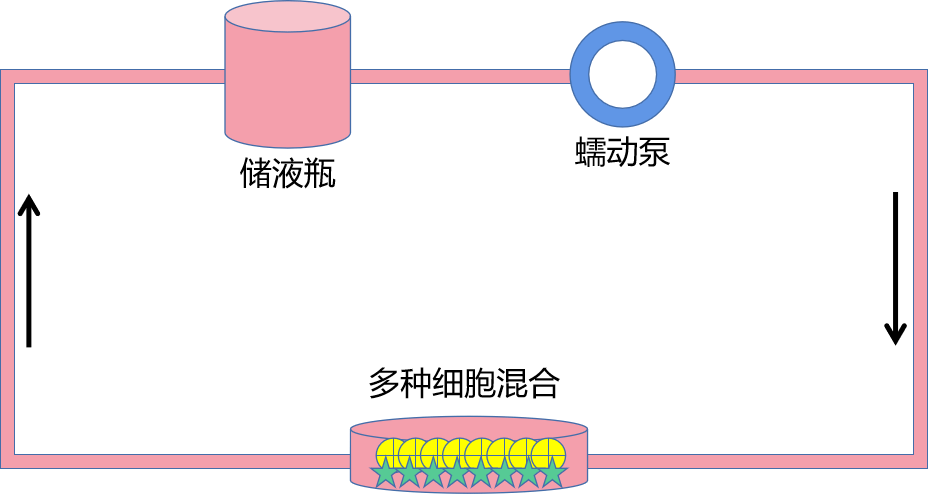
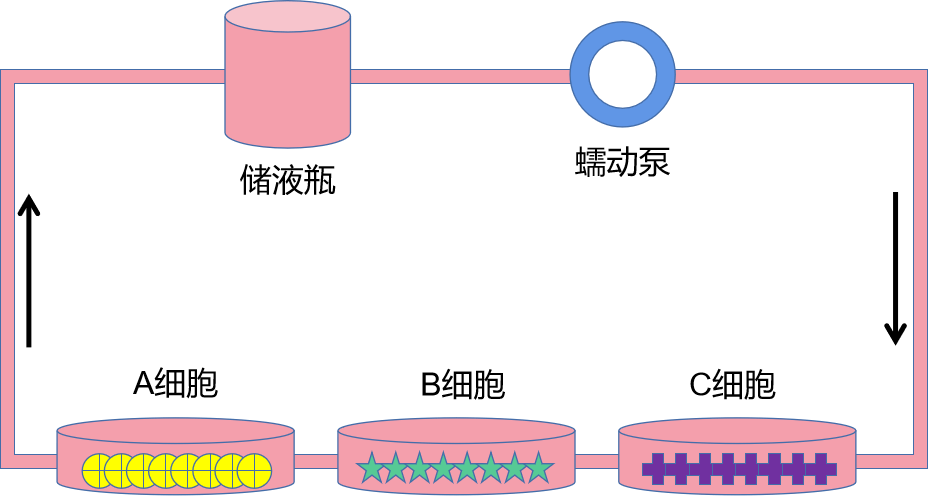
④多种细胞共培养,细胞间不直接接触,共用培养基
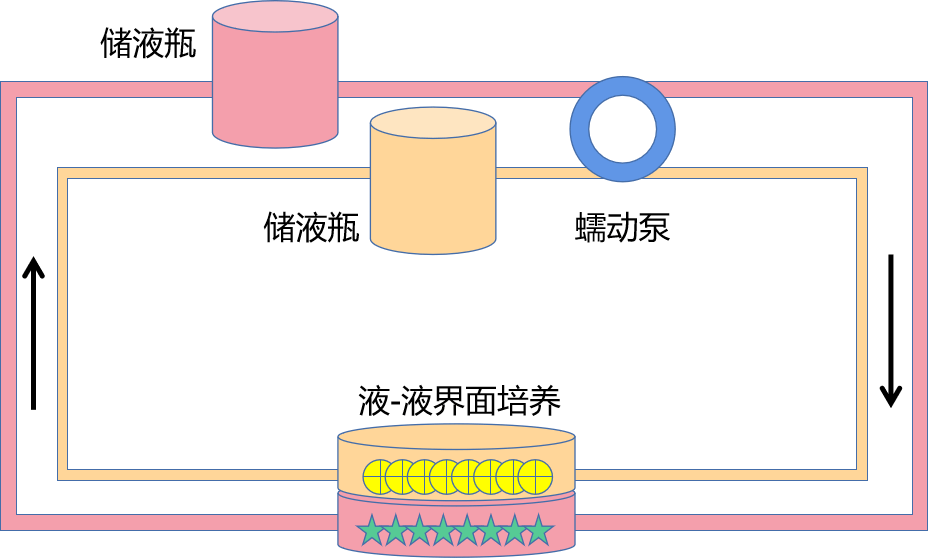
⑤用Transwell进行液-液界面培养(LLI)
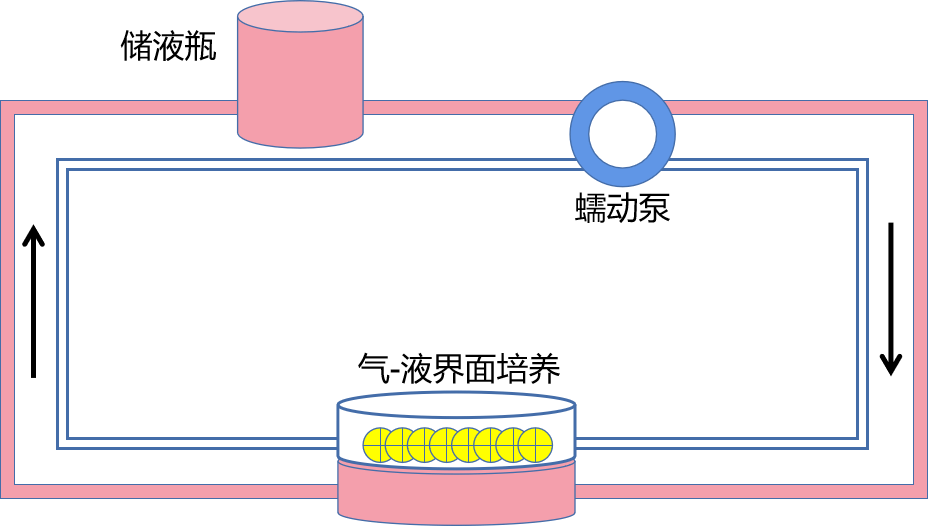
⑥用Transwell进行气-液界面培养(ALI)
⑦探索更多可能性:一个复杂的模型举例
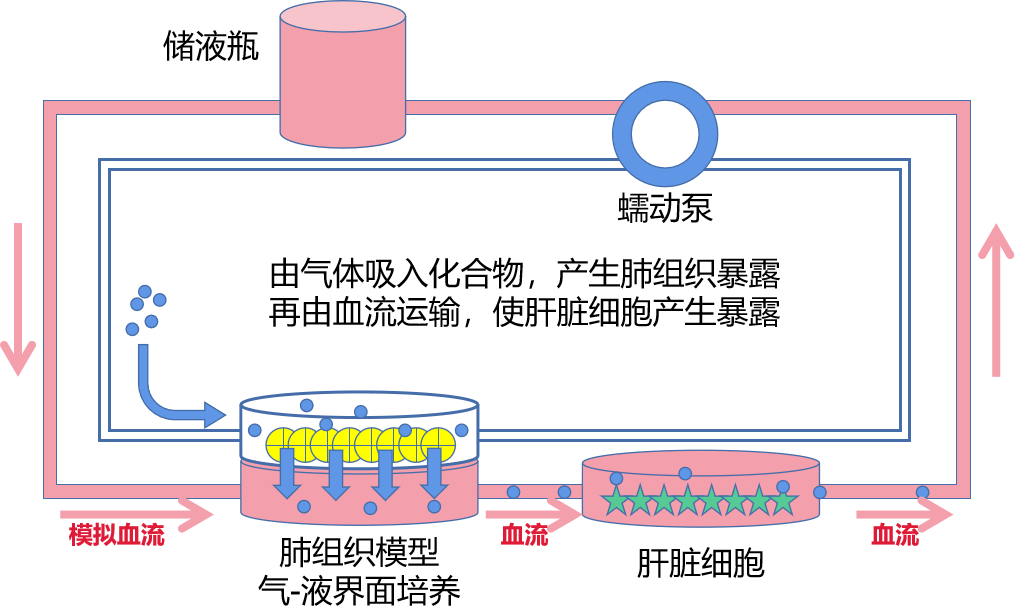
引用文献举例
1. Vinci, B. et al., 2011. Modular bioreactor for primary human hepatocyte culture: Medium flow stimulates expression and activity of detoxification genes.(培养人肝脏细胞:培养基流动可以促进解毒基因的表达) Biotechnology Journal, 6, pp.554–564.
2. Ramachandran, S.D. et al., 2015. In vitro generation of functional liver organoid-like structures using adult human cells(用成人肝脏细胞建立离体的有功能的肝脏类器官). PLoS ONE, 10(10).
3. Rashidi, H. et al., 2016. Fluid shear stress modulation of hepatocyte like cell function. (流体剪切力可以调节肝脏细胞功能)Archives of Toxicology, 90, 7.
4. Chandorkar, P. et al., 2017. Fast-track development of an in vitro 3D lung/immune cell model to study Aspergillus infections(研发离体的3D肺/免疫细胞模型,用于曲霉属真菌感染研究). Scientific Reports, 7, 11644.
5. Tommaso S. et al., 2011. Engineering Quasi-Vivo in vitro organ models.(建立Quasi Vivo离体器官模型) Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology Volume: 745, pp 138-153.
6. Patricia M. et al., 2018. A novel dynamic multicellular co-culture system for studying individual blood-brain barrier cell types in brain diseases and cytotoxicity testing.(一种创新的多细胞动态共培养系统,用于研究组成血脑屏障的各种细胞) Scientific Reports Volume: 8, Issue: 1, pp 8784.
7. Basma E. et al. 2020. A dynamic perfusion based blood-brain barrier model for cytotoxicity testing and drug permeation. (一种动态流动培养血脑屏障细胞模型,用于研究细胞毒性和药物通透性) Scientific Reports Volume: 10, Issue: 1, pp 3788.
8. Miranda A. et al., 2016. A three dimensional (3D) human in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB).(一种3D血脑屏障模型) Heart Volume: 102.
9. Buesch S. et al., 2018. A Novel In Vitro Liver Cell Culture Flow System Allowing Long-Term Metabolism and Hepatotoxicity Studies.(一种离体肝脏细胞流动培养新方法,可用于长时间的代谢和肝毒性研究) Applied In Vitro Toxicology Volume: 4, Issue: 3, pp 232-237.
10. Alec O. et al., 2019. Development of an in vitro media perfusion model of Leishmania major macrophage infection.(开发一种流动培养模型,用于利士曼原虫巨噬细胞感染的研究) 2019 PLOS ONE Volume: 14, Issue: 7.
11. Sean M. et al., 2017. In-silico Characterisation of the Kirkstall QV900 In-Vitro System for Advanced Cell Culture(对QV900用于体外培养的参数进行模拟计算). 5th International Conference on Computational and Mathematical Biomedical Engineering pp 1174-1177.
12. Ahluwalia A. et al., 2011. Hepatotoxicity of diclofenac in a Quasi-Vivo? multicompartment bioreactor(在流动培养条件下,检测双氯芬酸的肝毒性). Toxicology Letters Volume: 205.
13. Tomlinson, L. et al., 2019. In vitro liver zonation of primary rat hepatocytes.(用原代大鼠肝脏细胞进行的肝分区研究) Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 7(17).
14. Iori, E. et al., 2012. Glucose and fatty acid metabolism in a 3 tissue in-vitro model challenged with normo- and hyperglycaemia(建立一种正常血糖和高血糖条件下的三组织模型,研究糖和脂肪酸代谢). PLoS ONE, 7(4).
15. Mattei, G., Giusti, S. & Ahluwalia, A., 2014. Design Criteria for Generating Physiologically Relevant In Vitro Models in Bioreactors(在生物反应器中建立与生理状态类似的离体器官模型的设计标准). Processes, 2(3).
16. Mazzei, D. et al., 2010. A low shear stress modular bioreactor for connected cell culture under high flow rates(一种高流速低剪切力模块化细胞培养装置). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 106.
17. Vinci, B. et al., 2012. An in vitro model of glucose and lipid metabolism in a multicompartmental bioreactor(用Quasi Vivo流动培养系统研究糖和脂代谢). Biotechnology Journal, 7.
18. Nithiananthan, S. et al., 2016. Physiological Fluid Flow Moderates Fibroblast Responses to TGF-β1.(模拟生理条件的流动培养方式可以调节成纤维细胞对TGF-β1的反应) Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 13.