产品说明
销售土耳其INOVENSO科研级别到工业级别纳米纤维静电纺丝机
土耳其INOVENSO(Innovative Engineering Solutions)公司专注于专注纳米纤维及纳米纤维膜科研级、工业级的高效的纳米纤维以及纳米纤维膜产品的设计和制造,提供从任何实验规模的台式静电丝纺丝入门套件到中试实验室规模到半工业和工业规规模的静电纺及纳米纤维膜生产设备,其提供纳米静电纺丝设备和纳米纤维膜产品已成为纳米纤维学术界和工业界的桥梁,产品成熟度高、成功应用文献量达数百篇,在球拥有超过400个使用单位,并获得MIT,斯坦福大学,康奈尔大学等知名大学和3M等球公司的,霍尼韦尔(中国)和许多其他公司,和使用风险,是纳米纤维科学研究者的手选.
Inovenso使用特的专利“混合电纺技术”。这项新技术结合了基于针的技术和wu针技术的点,这些点包括:高生产效
率(来自wu针技术),对工艺和终产品的非常j确的控制(基于针技术) 。
适用于开发商用纳米纤维产品,例如面罩,电池隔板,空气和液体过滤器,伤口敷料等。
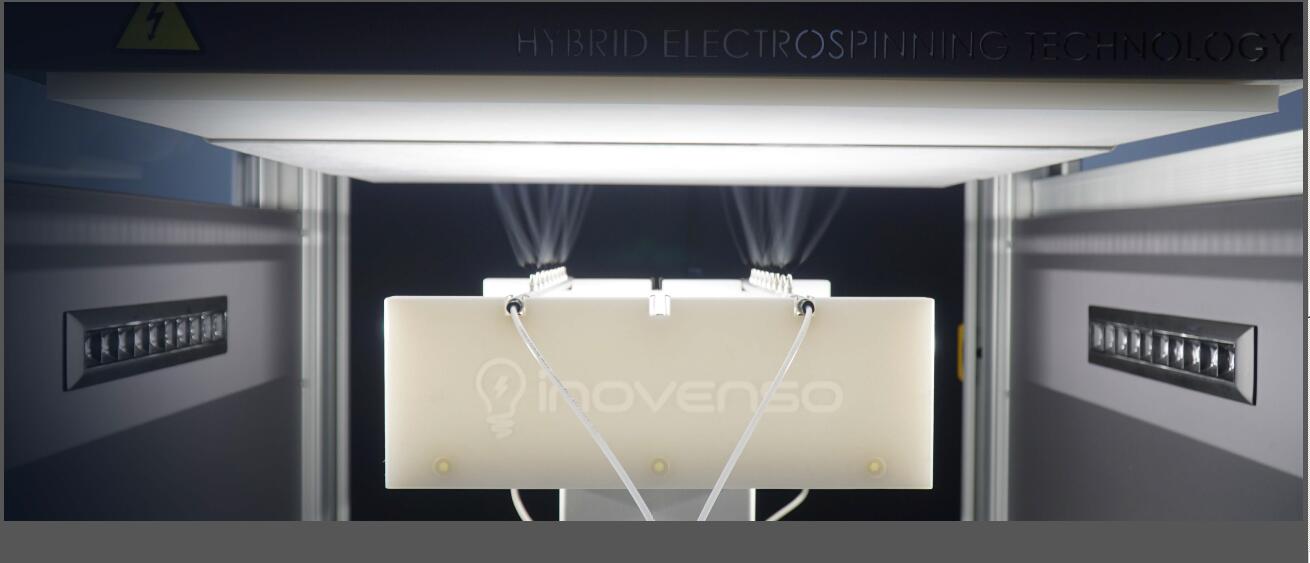

一、工业级别的纳米纤维静电纺生产线

1、 PE-3550型号的工业级纳米纤维生产线设备
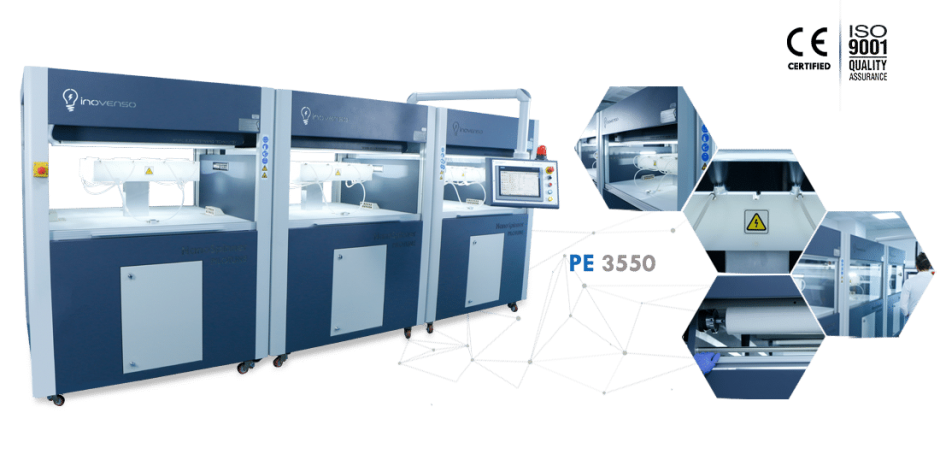

PE3550是一条纳米纤维生产线,可在卷对卷收集器上连续不断地实现高产量的纳米纤维。它由三个互连的PE 3550单元组成,可通过单个触摸屏面板进行调节。
PE3550适用于广泛的应用,初被认为是用于生产基于空气过滤纳米纤维的产品(N95 / N99过滤介质,HEPA / ULPA过滤器,汽车,HVAC等)。但是它也可以用于其他应用,例如:生物医学,制药,能源,纺织等。
PE3550配有168个静电纺丝喷嘴,使表面均匀且连续地形成550mm的宽度。得益于其的自动化系统和空调设备,即使在不断变化的环境条件下,它也能够以所需的质量进行连续生产。
du特的属性
自下而上的方式
可编程触摸屏控制面板
wanquan操作期间多可带56个喷嘴(每个单元)
可以单喷嘴工作
可选配标准不同直径的喷嘴
易于使用的1个精密蠕动泵(每个单元)
高通量纳米纤维生产可在更短的时间内实现更高的生产能力。
光纤沉积宽度:550毫米
基板卷绕速度:0.1 m / min – 10 m / min
2、NS 416 大规模工业级量产机型
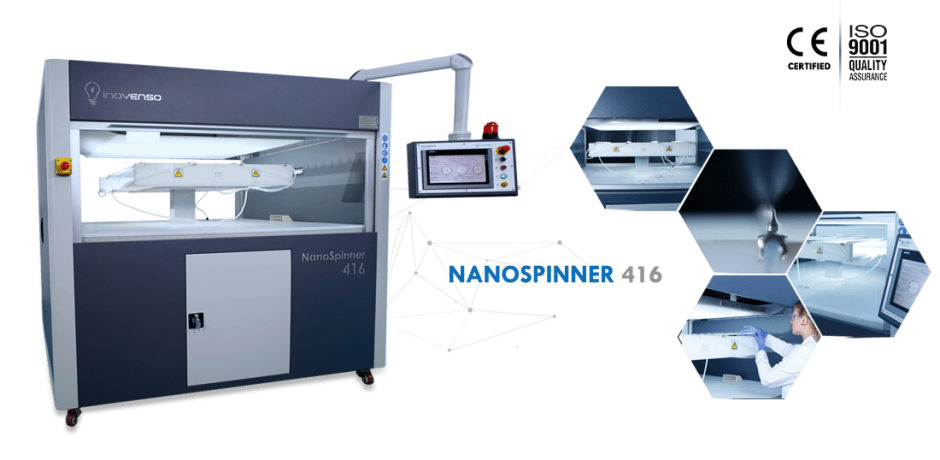
产量:2200-4400mL/小时, wu限制连续供液
精度范围:50-400 nm(0.05-0.4μm),平均精度:120nm
喷嘴数:132-264个,宽幅:100cm
二、PE-550/300工业级科研级两用灵活扩展性机型

三、小型

产量:500-1100mL/小时, wu限制连续供液
精度范围:50-400 nm(0.05-0.4μm),平均精度:120nm
喷嘴:18-36个,宽幅:300cm
应用及用户案例:
(二)、科研文献
-
Optimization of Electrospinning Parameters for Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Glycine Electrospun Nanofibers
Marwa Alazzawi, Nabeel Abid Alsahib and Hilal Turkoglu Sasmazel
Atilim University
-
Optimization of Electrospinning Parameters for Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Glycine Electrospun Nanofibers
Marwa Alazzawi, Nabeel Abid Alsahib and Hilal Turkoglu Sasmazel
Atilim University
-
Optimization of functionalized electrospun fibers for the development of colorimetric oxygen indicator as an intelligent food packaging system
Meryem Y?lmaz, Aylin Altan
Mersin University
-
Co-electrospun-electrosprayed PVA/folic acid nanofibers for transdermal drug delivery: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro cytocompatibility
Fatma Nur Parin, Cigdem Inci Aydemir, Gokce Taner, Kenan Yildirim
Bursa Technical University
-
5
Engineering multifunctional bactericidal nanofibers for abdominal hernia repair
Anderson Oliveira Lobo, Samson Afewerki
Harvard Medical School
-
6
An electrochemical immunosensor modified with titanium IV oxide/polyacrylonitrile nanofibers for the determination of carcino embriyonic antigen
Sema Aslan
Mu?la S?tk? Ko?man ?niversitesi
-
7
Polycaprolactone/silk fibroin electrospun nanofibers‐based lateral flow test strip for quick and facile determination of bisphenol A in breast milk
Begüm Gürel‐G?kmen, Hava Dudu Taslak, Ozan ?zcan, Necla ?par, Tu?ba Tunali‐Akbay
Marmara University
-
8
Electrospinning of ampicillin trihydrate loaded electrospun PLA nanofibers I: effect of polymer concentration and PCL addition on its morphology, drug delivery and mechanical properties
Tugba Eren Boncu, Nurten Ozdemir
Ankara University
-
9
Preparation of Silver Cyclohexane di Carboxylate: Β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes and Their Use in the Production of Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanowebs
R?za ATAV, Aylin YILDIZ, Derman VATANSEVER BAYRAMOL, Ahmet ?zgür A?IRGAN , U?ur ERG?NAY
Tekirda? Nam?k Kemal University
-
10
Holistic Investigation of the Electrospinning Parameters for High Percentage of β-phase in PVDF Nanofibers
Rahul Kumar Singh, Sun Woh Lye, Jianmin Miao
Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
-
11
Design and fabrication of nano-engineered electrospun filter media with cellulose nanocrystal for toluene adsorption from indoor air
Esra Buyukada-Kesici, Elifnur Gezmis-Yavuz, Dila Aydina, Elif Cansoy, Kadir Alp, Derya Y.Koseoglu-Imer
-
12
Biocomposite scaffolds for 3D cell culture: Propolis enriched polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers favoring cell adhesion
Rumeysa Bilginer, Dilce Ozkendir‐Inanc, Umit Hakan Yildiz, Ahu Arslan‐Yildiz
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/app.50287
-
13
Electrospun core-sheath PAN@ PPY nanofibers decorated with ZnO: photo-induced water decontamination enhanced by formation of a heterojunction
-
14
Dual electrospinning of a nanocomposites biofilm: Potential use as an antimicrobial barrier
Judith Vergara-Figueroa, Serguei Alejandro-Martin, Fabiola Cerda-Leal, William Gacitúa. Universidad del Bío-Bío
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2352492820326829
-
15
Helicoidally Arranged Polyacrylonitrile Fiber-Reinforced Strong and Impact-Resistant Thin Polyvinyl Alcohol Film Enabled by Electrospinning-Based Additive Manufacturing
Rahul Sahay , Komal Agarwal, Anbazhagan Subramani , Nagarajan Raghavan
https://scholar.google.com.tr/scholar_url?url=https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/12/10/2376/pdf&hl=tr&sa=X&d=15229915842923991540&ei=HfiNX_izGIy0ygT3m6bYBw&scisig=AAGBfm2QTPnRcmJgdY7WJqhwO9OTLvnGXA&nossl=1&oi=scholaralrt&hist=NSAhIeoAAAAJ:16172062561605054270:AAGBfm0NgWrUaFisOH1m3cVrJiuKCbAA7g&html=
-
16
Combinatorial effects of coral addition and plasma treatment on the properties of chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers intended for bone tissue engineering
-
17
Functional polymer nanofibers: from spinning fabrication techniques to recent biomedical applications
Danilo Martins dos Santos, Daniel S. Corrêa, Eliton S Medeiros, Juliano Oliveira, and LUIZ Henrique C. MATTOSO
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.0c12410
-
18
Composite Membranes with Nanofibrous Cross-hatched Supports for Reverse Osmosis Desalination
Seungju Kim , Daniel E. Heath, and Sandra E. Kentish
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.0c12588
-
19
A Bimodal Protein Fabric Enabled via In-Situ Diffusion for High-Performance Air Filtration
-
20
THE DEVELOPMENT AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLUORESCENT SENSORS FOR CONTINUOUS MONITORING OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOLECULES IN VIVO
-
21
Green seaweeds ulvan-cellulose scaffolds enhance in vitro cell growth and in vivo angiogenesis for skin tissue engineering
Koushanee Madub Nowsheen Goonoo Fanny Gimié Imade Ait Arsa HolgerSch?nherr Archana Bhaw-Luximon
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S014486172031198X
-
22
Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity evaluation of electrospun PCL nanofiber composites of resveratrol nanocrystals
-
23
Electrospinning of PLA and PLA/POSS nanofibers: Use of Taguchi optimization for process parameters
-
24
Centella Asiatica Extract Containing Bilayered Electrospun Wound Dressing
Ismail Alper Isoglu & Nuray Koc
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12221-020-9956-y
-
25
Heterogeneous PVC cation-exchange membrane synthesis by electrospinning for reverse electrodialysis
JS Jaime-Ferrer, M Mosqueda-Quintero
https://www.degruyter.com/view/journals/ijcre/ahead-of-print/article-10.1515-ijcre-2020-0020/article-10.1515-ijcre-2020-0020.xml
-
26
Electrochemical evaluation of Titanium (IV) Oxide/Polyacrylonitrile electrospun discharged battery coals as supercapacitor electrodes
Sema Aslan, Derya Bal Altunta?, ?a?da? Ko?ak, Hülya Kara Suba?at
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/elan.202060239
-
27
Progress in the design and development of “fast-dissolving” electrospun nanofibers based drug delivery systems - A systematic review
-
28
Stabilizing 3 nm-Pt nanoparticles in close proximity on rutile nanorods-decorated-TiO2 nanofibers by improving support uniformity for catalytic reactions
Wanlin Fu, Zhihui Li, Yunpeng Wang, Yueming Sun, Yunqian Dai. Southeast University, Nanjing.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1385894720321410#!
-
29
Photoluminescence Properties of a New Sm(III) Complex/PMMA Electrospun Composite Fibers
Hulya Kara, Gorkem Oylumluoglu & Mustafa Burak Coban. Balikesir University.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10876-019-01677-7
-
30
Optimization of the electrospinning process variables for gelatin/silver nanoparticles/bioactive glass nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering
Aysen Akturk, Melek Erol Taygun, Gultekin Goller Istanbul Technical University Scientific Research Projects Foundation, Grant/Award Number: 38881
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pc.25545
-
31
Preparation And Characterization Of Polyvinyl Borate/Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVB/PVA) Blend Nanofibers
Koysuren, O., Karaman, M. and Dinc, H. (2012), Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl borate/polyvinyl alcohol (PVB/PVA) blend nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 124: 2736–2741. doi:10.1002/app.35035
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/app.35035/full)
-
32
The Effects of Power and Feeding Rate on Production of Polyurethane Nanofiber with Electrospinning Process
O?teyaka, M. O., O?zel, E., Y?ld?r?m, M. M., Aslan, M. H., Oral, A. Y., O?zer, M., & C?aglar, S. H. (2011). The Effects of Power and Feeding Rate on Production of Polyurethane Nanofiber with Electrospinning Process. doi:10.1063/1.3663116
(https://aip.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1063/1.3663116)
-
33
Initiated Chemical Vapor Deposition Of Ph Responsive Poly(2-Diisopropylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate Thin Films
Mustafa Karaman, Nihat ?abuk, Initiated chemical vapor deposition of pH responsive poly(2-diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate thin films, Thin Solid Films, Volume 520, Issue 21, 31 August 2012, Pages 6484-6488, ISSN 0040-6090, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2012.06.083
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040609012008140)
-
34
S?cak Filament Destekli Kimyasal Buhar Biriktirme Y?ntemi ?le Süper Su ?tici Nano Kaplama Sentezi
?abuk, N. (2012). S?cak filament destekli kimyasal buhar biriktirme y?ntemi ile süper su itici nano kaplama sentezi (Doctoral dissertation, Sel?uk ?niversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü).
(http://acikerisim.selcuk.edu.tr:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/1151)
-
35
Preparation And Characterization Of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Carbon Nanotube (PVA/CNT) Conductive Nanofibers
K?ysüren, O. (2012). Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/carbon nanotube (PVA/CNT) conductive nanofibers. Journal of Polymer Engineering, 32(6-7), pp. 407-413. Retrieved 29 Apr. 2016, from doi:10.1515/polyeng-2012-0068
(http://www.degruyter.com/view/j/polyeng.2012.32.issue-6-7/polyeng-2012-0068/polyeng-2012-0068.xml)
-
36
The development and design of fluorescent sensors for continuous in vivo glucose monitoring
Balaconis, Mary K., “The development and design of fluorescent sensors for continuous in vivo glucose monitoring” (2014). Mechanical Engineering Dissertations. Paper 54.
(http://hdl.handle.net/2047/d20004844)
-
37
Effects of different sterilization methods on polyester surfaces
Duzyer, Sebnem & Koral Ko?, Serpil & Hockenberger, Asli & Evke, Elif & Kahveci, Zeynep & Uguz, Agah. (2013). Effects of different sterilization methods on polyester surfaces. Tekstil ve Konfeksiyon. 23. 319-324.
(https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272672175_Effects_of_different_sterilization_methods_on_polyester_surfaces)
-
38
Polymer Nanofibers: Building Blocks for Nanotechnology
Pisignano, D. (2013). Polymer nanofibers: building blocks for nanotechnology. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry.
(https://books.google.com.tr/books?id=BnQoDwAAQBAJ&hl=tr)
-
39
Affecting Parameters On Electrospinning Process And Characterization Of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers
Nagihan Okutan, P?nar Terzi, Filiz Altay, Affecting parameters on electrospinning process and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers, Food Hydrocolloids, Volume 39, August 2014, Pages 19-26, ISSN 0268-005X, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.12.022.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268005X13004062)
-
40
Design Of A Novel Nozzle Prototype For Increased Productivity And Improved Coating Quality During Electrospinning
UCAR, Nuray; UCAR, Mehmet; KIZILDA?, Nuray. DESIGN OF A NOVEL NOZZLE PROTOTYPE FOR INCREASED PRODUCTIVITY AND IMPROVED COATING QUALITY DURING ELECTROSPINNING. Journal of Textile & Apparel/Tekstil ve Konfeksiyon, 2013, 23.3.
(https://www.researchgate.net/publication/293543273_DESIGN_OF_A_NOVEL_NOZZLE_PROTOTYPE_FOR_INCREASE_PRODUCTIVITY_AND_IMPROVED_COATING_QUALITY_DURING_ELECTROSPINNING)
-
41
Electrospun Polyvinyl Borate/Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PVB/PMMA) Blend Nanofibers
Koysuren, O., Karaman, M., Yildiz, H. B., Koysuren, H. N., & Din?, H. (2014). Electrospun polyvinyl borate/poly (methyl methacrylate)(PVB/PMMA) blend nanofibers. International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials, 63(7), 337-341.
(http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00914037.2013.845188)
-
42
Industrial Upscaling of Electrospinning and Applications of Polymer Nanofibers: A Review
Persano, L., Camposeo, A., Tekmen, C., & Pisignano, D. (2013). Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nanofibers: a review.Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 298(5), 504-520.
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mame.201200290/full)
-
Template Assisted Synthesis Of Photocatalytic Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes By Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition Method
Mustafa Karaman, Fatma Sar?ipek, ?zcan K?ysüren, H. Bekir Y?ld?z, Template assisted synthesis of photocatalytic titanium dioxide nanotubes by hot filament chemical vapor deposition method, Applied Surface Science, Volume 283, 15 October 2013, Pages 993-998, ISSN 0169-4332, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.07.058.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016943321301369X)
-
44
UV Illumination Effects On Electrical Characteristics Of Metal–Polymer–Semiconductor Diodes Fabricated With New Poly(Propylene Glycol)-B-Polystyrene Block Copolymer
G?k?en, M. Y?ld?r?m, A. Demir, A. All?, S. All?, B. Hazer, UV illumination effects on electrical characteristics of metal–polymer–semiconductor diodes fabricated with new poly(propylene glycol)-b-polystyrene block copolymer, Composites Part B: Engineering, Volume 57, February 2014, Pages 8-12, ISSN 1359-8368, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.09.038.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1359836813005519)
-
Experimental Study on Relationship of Applied Power And Feeding Rate on Production of Polyurethane Nanofibre
Oteyaka, M., Ozel, E., & Y?ld?r?m, M. (2014). Experimental Study On Relationship Of Applied Power And Feeding Rate On Production Of Polyurethane Nanofibre. Gaz? Un?vers?ty Journal Of Sc?ence, 26(4), 611-618.
(http://gujs.gazi.edu.tr/article/view/1060000855)
-
46
Electrospun Fibers For Vaginal Anti-HIV Drug Delivery
Anna K. Blakney, Cameron Ball, Emily A. Krogstad, Kim A. Woodrow, Electrospun fibers for vaginal anti-HIV drug delivery, Antiviral Research, Volume 100, Supplement, December 2013, Pages S9-S16, ISSN 0166-3542, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.09.022.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166354213002829)
-
47
Polivinil Borat Sentezin ; Elektrospin Y?ntemiyle Nanofiber Haz?rlanmas? Ve Karakterizasyonu
Din?, H. (2013). Polivinil borat sentezin; elektrospin y?ntemiyle nanofiber haz?rlanmas? ve karakterizasyonu (Doctoral dissertation, Sel?uk ?niversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü).
(http://acikerisim.selcuk.edu.tr:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/1158)
-
48
Commercial Viability Analysis of Lignin Based Carbon Fibre
Chen, M.C. (2014). Commercial Viability Analysis of Lignin Based Carbon Fibre.
(https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/56378549.pdf)
-
49
Electrospun Antibacterial Nanofibers: Production, Activity, And In Vivo Applications
Gao, Y., Bach Truong, Y., Zhu, Y. and Louis Kyratzis, I. (2014), Electrospun antibacterial nanofibers: Production, activity, and in vivo applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 131, 40797, doi: 10.1002/app.40797
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/app.40797/full)
-
50
Glucose-sensitive nanofiber scaffolds with an improved sensing design for physiological conditions
Balaconis, M. K., Luo, Y., & Clark, H. A. (2015). Glucose-sensitive nanofiber scaffolds with an improved sensing design for physiological conditions. The Analyst, 140(3), 716–723. doi:10.1039/c4an01775g
(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/AN/C4AN01775G#!divAbstract)
-
51
Utilization Of Electrospun Nanofibers Containing Gelatin Or Gelatin-cellulose Acetate For Preventing Syneresis In Tomato Ketchup
Hendessi, S. (2014). Jelat?n Veya Jelat?n-selüloz Asetat ??eren Nanoliflerin Domates Ket?aplar?nda Sineresisi ?nleyici Olarak Kullan?lmas? (Doctoral dissertation, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü).
(http://hdl.handle.net/11527/2193)
-
52
Thermal Conductivity Of Electrospun Polyethylene Nanofibers
Ma, J., Zhang, Q., Mayo, A., Ni, Z., Yi, H., Chen, Y., … & Li, D. (2015). Thermal conductivity of electrospun polyethylene nanofibers. Nanoscale, 7(40), 16899-16908.
(http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/nr/c5nr04995d#!divAbstract)
-
53
Chloroform-Formic Acid Solvent Systems for Nanofibrous Polycaprolactone Webs
Enis, I. Y., Vojtech, J., & Sadikoglu, T. G. (2015). Chloroform-Formic Acid Solvent Systems for Nanofibrous Polycaprolactone Webs. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, International Journal of Environmental, Chemical, Ecological, Geological and Geophysical Engineering, 9(5), 429-432.
(http://www.waset.org/publications/10001167)
-
54
Preparation And In Vitro Characterization Of Electrospun 45S5 Bioactive Glass Nanofibers
Aylin M. Deliormanl?, Preparation and in vitro characterization of electrospun 45S5 bioactive glass nanofibers, Ceramics International, Volume 41, Issue 1, Part A, January 2015, Pages 417-425, ISSN 0272-8842, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.08.086.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272884214013236)
-
55
Towards Scalable Binderless Electrodes: Carbon Coated Silicon Nanofiber Paper via Mg Reduction of Electrospun SiO2 Nanofibers
Favors, Z., Bay, H. H., Mutlu, Z., Ahmed, K., Ionescu, R., Ye, R., … & Ozkan, C. S. (2015). Towards scalable binderless electrodes: carbon coated silicon nanofiber paper via Mg reduction of electrospun SiO2 nanofibers. Scientific reports, 5.
(http://www.nature.com/articles/srep08246?message-global=remove&WT.ec_id=SREP-639-20150210)
-
56
Cellulose Acetate–Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Functional Surfaces with Temperature-Triggered Switchable Wettability
Ganesh, V. A., Ranganath, A. S., Sridhar, R., Raut, H. K., Jayaraman, S., Sahay, R., … & Baji, A. (2015). Cellulose Acetate–Poly (N‐isopropylacrylamide)‐Based Functional Surfaces with Temperature‐Triggered Switchable Wettability. Macromolecular rapid communications, 36(14), 1368-1373.
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/marc.201500037/abstract?userIsAuthenticated=false&deniedAccessCustomisedMessage=)
-
57
Electrospinning Of Nanofibrous Polycaprolactone (PCL) And Collagen-Blended Polycaprolactone For Wound Dressing And Tissue Engineering
Zeybek, B., Duman, M., & ?rkmez, A. S. (2014). Electrospinning of nanofibrous polycaprolactone (PCL) and collagen-blended polycaprolactone for wound dressing and tissue engineering. Usak University Journal of Material Sciences, 3(1), 121.
(http://search.proquest.com/openview/ecfe94e89a75c0739c7fd72ba51bf90f/1?pq-origsite=gscholar)
-
58
Phosphine-Functionalized Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Silica Nanofibers As Highly Effective Adsorbent For Removal Of Aqueous Manganese And Nickel Ions
Md. Shahidul Islam, Md. Saifur Rahaman, Jeong Hyun Yeum, Phosphine-functionalized electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica nanofibers as highly effective adsorbent for removal of aqueous manganese and nickel ions, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, Volume 484, 5 November 2015, Pages 9-18, ISSN 0927-7757, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.07.023.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092777571530100X)
-
59
Free-Standing Ni–Nio Nanofiber Cloth Anode For High Capacity And High Rate Li-Ion Batteries
Jeffrey Bell, Rachel Ye, Kazi Ahmed, Chueh Liu, Mihrimah Ozkan, Cengiz S. Ozkan, Free-standing Ni–NiO nanofiber cloth anode for high capacity and high rate Li-ion batteries, Nano Energy, Volume 18, November 2015, Pages 47-56, ISSN 2211-2855, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.09.013.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211285515003742)
-
60
Coaxial Electrospinning Of WO3 Nanotubes Functionalized With Bio-?nspired Pd Catalysts And Their Superior Hydrogen Sensing Performance
Choi, S. J., Chattopadhyay, S., Kim, J. J., Kim, S. J., Tuller, H. L., Rutledge, G. C., & Kim, I. D. (2016). Coaxial electrospinning of WO 3 nanotubes functionalized with bio-inspired Pd catalysts and their superior hydrogen sensing performance. Nanoscale.
(http://pubs.rsc.org/is/content/articlelanding/2016/nr/c5nr06611e/unauth#!divAbstract)
-
61
Electrospun Cerium And Gallium-Containing Silicate Based 13-93 Bioactive Glass Fibers For Biomedical Applications
Aylin M. Deliormanl?, Electrospun cerium and gallium-containing silicate based 13-93 bioactive glass fibers for biomedical applications, Ceramics International, Volume 42, Issue 1, Part A, January 2016, Pages 897-906, ISSN 0272-8842, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.09.016.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272884215017241)
-
62
Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/ Pluronic F127 Blended Nanofibers Containing Titanium Dioxide For Antibacterial Wound Dressing
El-Aassar, M. R., El-Deeb, N. M., Hassan, H. S., & Mo, X. (2015). Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/Pluronic F127 Blended Nanofibers Containing Titanium Dioxide for Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 1-15.
(http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12010-015-1962-y)
-
63
Preparation, In Vitro Mineralization And Osteoblast Cell Response Of Electrospun 13–93 Bioactive Glass Nanofibers
Aylin M. Deliormanl?, Preparation, in vitro mineralization and osteoblast cell response of electrospun 13–93 bioactive glass nanofibers, Materials Science and Engineering: C, Volume 53, 1 August 2015, Pages 262-271, ISSN 0928-4931, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.04.037.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493115300394)
-
64
Membrane manufacturing via simultaneous electrospinning of PAN and PSU solutions
Guclu, S., Pasaoglu, M. E., & Koyuncu, I. (2015). Membrane manufacturing via simultaneous electrospinning of PAN and PSU solutions. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1-9.
(http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19443994.2015.1024747)
-
65
Applying Nanotechnology to the Desulfurization Process in Petroleum Engineering
Ogunlaja, A. S., & Tshentu, Z. R. (2015). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanofibers for Adsorptive Desulfurization. Applying Nanotechnology to the Desulfurization Process in Petroleum Engineering, 281.
(https://books.google.com.tr/books?hl=tr&lr=&id=oGa2CgAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA281&dq=inovenso&ots=D8gIXZpcRB&sig=V_3qD1gM2EfbBpWrKSkxMgXhGGA&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=inovenso&f=false)
-
66
Investigation of wettability and moisture sorption property of electrospun poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanofibers
Ranganath, A. S., Ganesh, V. A., Sopiha, K., Sahay, R., & Baji, A. Investigation of wettability and moisture sorption property of electrospun poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) nanofibers. MRS Advances, 1-6.
(http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=10198457&fileId=S205985211600164X)
-
67
Alternative Solvent Systems For Polycaprolactone Nanowebs Via Electrospinning
Ipek Y Enis, Jakub Vojtech, and Telem G Sadikoglu, Alternative solvent systems for polycaprolactone nanowebs via electrospinning, Journal of Industrial Textiles 1528083716634032, first published on February 17, 2016 doi:10.1177/1528083716634032
(http://jit.sagepub.com/content/early/2016/02/17/1528083716634032.abstract)
-
68
Controlled Release Of A Hydrophilic Drug From Coaxially Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers
Zahida Sultanova, Gizem Kaleli, G?zde Kabay, Mehmet Mutlu, Controlled release of a hydrophilic drug from coaxially electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Volume 505, Issues 1–2, 30 May 2016, Pages 133-138, ISSN 0378-5173, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.03.032.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378517316302320)
-
69
Recent Developments In Micro- And Nanofabrication Techniques For The Preparation Of Amorphous Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
Sheng Qi, Duncan Craig, Recent developments in micro- and nanofabrication techniques for the preparation of amorphous pharmaceutical dosage forms, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, Available online 9 January 2016, ISSN 0169-409X, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.01.003.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169409X16300059)
-
70
Fabrication Of Electrospun Nanofiber Catalysts And Ammonia Borane Hydrogen Release Efficiency
Bilge Co?kuner Filiz, Aysel Kantürk Figen, Fabrication of electrospun nanofiber catalysts and ammonia borane hydrogen release efficiency, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Available online 18 April 2016, ISSN 0360-3199, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.182.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360319915318632)
-
71
Enhancement Of Mechanical And Physical Properties Of Electrospun PAN Nanofiber Membranes Using PVDF Particles
Elkhaldi, R. M., Guclu, S., & Koyuncu, I. (2016). Enhancement of mechanical and physical properties of electrospun PAN nanofiber membranes using PVDF particles. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1-11.
(http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19443994.2016.1159253)
-
72
Proposal Of A Framework For Scale-Up Life Cycle Inventory: A Case Of Nanofibers For Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Applications
Simon, B., Bachtin, K., Kili?, A., Amor, B., & Weil, M. (2016). Proposal of a framework for scale‐up life cycle inventory: A case of nanofibers for lithium iron phosphate cathode applications. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management. doi: [10.1002/ieam.1788].
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ieam.1788/abstract)
-
73
Electrospun Differential Wetting Membranes for Efficient Oil–Water Separation
Ganesh, V. A., Ranganath, A. S., Baji, A., Wong, H. C., Raut, H. K., Sahay, R., & Ramakrishna, S. (2016). Electrospun Differential Wetting Membranes for Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering.
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mame.201600074/abstract)
-
74
On the adhesion of hierarchical electrospun fibrous structures and prediction of their pull-off strength
Sahay, R., Parveen, H., Ranganath, A. S., Ganesh, V. A., & Baji, A. (2016). On the adhesion of hierarchical electrospun fibrous structures and prediction of their pull-off strength. RSC Advances, 6(53), 47883–47889. doi:10.1039/c6ra05757h
(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/RA/c6ra05757h#!divAbstract)
-
75
Fabrication of nanocomposite mat through incorporating bioactive glass particles into gelatin/poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers by using Box–Behnken design
G?nen, S. ?., Erol Taygun, M., Aktürk, A., & Kü?ükbayrak, S. (2016). Fabrication of nanocomposite mat through incorporating bioactive glass particles into gelatin/poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers by using Box–Behnken design. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 67, 684–693. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2016.05.065
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493116304982)
-
76
Ca3(PO4)2 precipitated layering of an in situ hybridized PVA/Ca2O4Si nanofibrous antibacterial wound dressing
Mabrouk, M., Choonara, Y. E., Marimuthu, T., Kumar, P., du Toit, L. C., van Vuuren, S., & Pillay, V. (2016). Ca3(PO4)2 precipitated layering of an in situ hybridized PVA/Ca2O4Si nanofibrous antibacterial wound dressing. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 507(1-2), 41–49. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.05.011
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378517316303751?via%3Dihub)
-
77
Fabrication of protein scaffold by electrospin coating for artificial tissue
Ozcan, F., Ertul, S., & Maltas, E. (2016). Fabrication of protein scaffold by electrospin coating for artificial tissue. Materials Letters, 182, 359–362. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2016.07.010
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167577X16311065)
-
78
Comparative Study of Poly (ε-Caprolactone) and Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) -Based Nanofiber Scaffolds for pH-Sensing
Di, W., Czarny, R. S., Fletcher, N. A., Krebs, M. D., & Clark, H. A. (2016). Comparative Study of Poly (ε-Caprolactone) and Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) -Based Nanofiber Scaffolds for pH-Sensing. Pharmaceutical Research, 33(10), 2433–2444. doi:10.1007/s11095-016-1987-0
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11095-016-1987-0)
-
79
Preparation and characterization of electrospun nanofibers containing glutamine
Tort, S., & Acartürk, F. (2016). Preparation and characterization of electrospun nanofibers containing glutamine. Carbohydrate Polymers, 152, 802–814. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.028
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0144861716308177)
-
80
Yap?l? Poli(Akrilonitril-Vinil Asetat)/Grafen Oksit Yap?lar?n Karakterizasyonu
T?YEK, ? , YAZICI, M , ALMA, M , D?NMEZ, U , YILDIRIM, B , SALAN, T , URU?, S , KARATA?, ? , KARTER?, ? . (2016). Nanolif Yap?l? Poli (Akrilonitril-Vinil Asetat)/ Grafen Oksit Yap?lar?n Karakterizasyonu. Tekstil ve Mühendis, 23 (102), 0-0.
(https://dergipark.org.tr/teksmuh/issue/24718/261437)
-
81
Durable adhesives based on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers
Sahay, R., Baji, A., Ranganath, A. S., & Anand Ganesh, V. (2016). Durable adhesives based on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 134(2). doi:10.1002/app.44393
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/app.44393)
-
82
Electrospinning—Commercial Applications, Challenges and Opportunities
Kannan, B., Cha, H., & Hosie, I. C. (2016). Electrospinning—Commercial Applications, Challenges and Opportunities. Nano-Size Polymers, 309–342. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-39715-3_11
(https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-39715-3_11)
-
83
US20160274030A1 Compositions and methods for measurement of analytes
Northeastern University, Boston, MA(US) (2016). Compositions and methods for measurement of analytes. US20160274030A1.
(https://patents.google.com/patent/US20160274030A1/en)
-
84
Effect Of Ethylene Oxide, Autoclave and Ultra Violet Sterilizations On Surface Topography Of Pet Electrospun Fibers
Sebnem DUZYER [1], Asli HOCKENBERGER [2], Agah UGUZ [3], Elif EVKE [4], ZeynepKAHVEC? [5]. 358 412. Uluda? University Journal of The Faculty of Engineering, 21 (2), 201-218. DOI: 10.17482/uujfe.04230
(https://doi.org/10.17482/uujfe.04230)
-
85
Fabrication of PVDF hierarchical fibrillar structures using electrospinning for dry-adhesive applications
Sahay, R., Parveen, H., Baji, A., Ganesh, V. A., & Ranganath, A. S. (2016). Fabrication of PVDF hierarchical fibrillar structures using electrospinning for dry-adhesive applications. Journal of Materials Science, 52(5), 2435–2441. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0537-9
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10853-016-0537-9)
-
86
Investigation of in vitro mineralization of silicate-based 45S5 and 13-93 bioactive glasses in artificial saliva for dental applications
Deliormanl?, A. M. (2017). Investigation of in vitro mineralization of silicate-based 45S5 and 13-93 bioactive glasses in artificial saliva for dental applications. Ceramics International, 43(4), 3531–3539. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.11.078
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272884216320697)
-
87
Hierarchical Structured Electrospun Nanofibers for Improved Fog Harvesting Applications
Ganesh, V. A., Ranganath, A. S., Baji, A., Raut, H. K., Sahay, R., & Ramakrishna, S. (2016). Hierarchical Structured Electrospun Nanofibers for Improved Fog Harvesting Applications. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 302(2), 1600387. doi:10.1002/mame.201600387
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mame.201600387)
-
88
A comparative study for lipase immobilization onto alginate based composite electrospun nanofibers with effective and enhanced stability
?spirli Do?a?, Y., Deveci, ?., Mercimek, B., & Teke, M. (2017). A comparative study for lipase immobilization onto alginate based composite electrospun nanofibers with effective and enhanced stability. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 96, 302–311. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.120
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141813016319572)
-
89
Crystallisation of amorphous fenofibrate and potential of the polymer blend electrospun matrices to stabilise in its amorphous form
Tipduangta, P. (2016). Retrieved from https://ueaeprints.uea.ac.uk/61721/
(https://ueaeprints.uea.ac.uk/61721/)
-
90
Smartphone-based detection of dyes in water for environmental sustainability
Smartphone-based detection of dyes in water for environmental sustainability. Analytical Methods, 9(4), 579–585. doi:10.1039/c6ay03073d
(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/ay/c6ay03073d/unauth#!divAbstract)
-
91
Tailoring of Architecture and Intrinsic Structure of Electrospun Nanofibers by Process Parameters for Tissue Engineering Applications
Kolbuk, D. (2016). Tailoring of Architecture and Intrinsic Structure of Electrospun Nanofibers by Process Parameters for Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanofiber Research – Reaching New Heights. doi:10.5772/64177
(http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/64177)
-
92
Physical and Chemical Properties of Poly (l-lactic acid)/Graphene Oxide Nanofibers for Nerve Regeneration
?ztatl?, H., & Ege, D. (2016). Physical and Chemical Properties of Poly (l-lactic acid)/Graphene Oxide Nanofibers for Nerve Regeneration. MRS Advances, 2(24), 1291–1296. doi:10.1557/adv.2016.663
(https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.663)
-
93
Drug Delivery and Development of Anti-HIV Microbicides
das Neves, J. (Ed.), Sarmento, B. (Ed.). (2015). Drug Delivery and Development of Anti-HIV Microbicides. New York: Jenny Stanford Publishing, https://doi.org/10.1201/b17559
(https://doi.org/10.1201/b17559)
-
94
Thin film composite membranes for forward osmosis supported by commercial nanofiber nonwovens
Maqsud R. Chowdhury, Liwei Huang, and Jeffrey R. McCutcheon
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2017 56 (4), 1057-1063
DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b04256
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b04256)
-
95
Dry-adhesives based on hierarchical poly (methyl methacrylate) electrospun fibers
Sahay, R., Baji, A., Parveen, H., & Ranganath, A. S. (2017). Dry-adhesives based on hierarchical poly(methyl methacrylate) electrospun fibers. Applied Physics A, 123(3). doi:10.1007/s00339-017-0816-6
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00339-017-0816-6)
-
96
Fabrication and characterization of electrospun poly(e-caprolactone) fibrous membrane with antibacterial functionality
Cerkez I, Sezer A, Bhullar SK. 2017 Fabrication and characterization of electrospun poly(e-caprolactone) fibrous membrane with antibacterial functionality.R. Soc. open sci. 4: 160911. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsos.160911
(https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10.1098/rsos.160911)
-
97
Recent Advances in Needleless Electrospinning of Ultrathin Fibers: From Academia to Industrial Production
Yu, M., Dong, R.-H., Yan, X., Yu, G.-F., You, M.-H., Ning, X., & Long, Y.-Z. (2017). Recent Advances in Needleless Electrospinning of Ultrathin Fibers: From Academia to Industrial Production. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 302(7), 1700002. doi:10.1002/mame.201700002
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mame.201700002)
-
98
Thermoresponsive electrospun membrane with enhanced wettability
Ranganath, A. S., Ganesh, V. A., Sopiha, K., Sahay, R., & Baji, A. (2017). Thermoresponsive electrospun membrane with enhanced wettability. RSC Adv., 7(32), 19982–19989. doi:10.1039/c6ra27848e
(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2017/ra/c6ra27848e)
-
99
Electrospun Bead-On-String Hierarchical Fibers for Fog Harvesting Application
Thakur, N., Ranganath, A. S., Agarwal, K., & Baji, A. (2017). Electrospun Bead-On-String Hierarchical Fibers for Fog Harvesting Application. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 302(7), 1700124. doi:10.1002/mame.201700124
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mame.201700124)
-
100
Three-Dimensional Au-Coated Electrosprayed Nanostructured BODIPY Films on Aluminum Foil as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Platforms and Their Catalytic Applications
Yilmaz, M., Erkartal, M., Ozdemir, M., Sen, U., Usta, H., & Demirel, G. (2017). Three-Dimensional Au-Coated Electrosprayed Nanostructured BODIPY Films on Aluminum Foil as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Platforms and Their Catalytic Applications. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9(21), 18199–18206. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b03042
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.7b03042)
-
101
A high flux polyvinyl acetate-coated electrospun nylon 6/SiO2 composite microfiltration membrane for the separation of oil-in-water emulsion with improved antifouling performance
Islam, M. S., McCutcheon, J. R., & Rahaman, M. S. (2017). A high flux polyvinyl acetate-coated electrospun nylon 6/SiO 2 composite microfiltration membrane for the separation of oil-in-water emulsion with improved antifouling performance. Journal of Membrane Science, 537, 297–309. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2017.05.019
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.7b03042)
-
102
Effect of pillar aspect ratio on shear adhesion strength of hierarchical electrospun fibrous structures
Sahay, R., & Baji, A. (2017). Effect of pillar aspect ratio on shear adhesion strength of hierarchical electrospun fibrous structures. Journal of Materials Science, 52(17), 10592–10599. doi:10.1007/s10853-017-1191-6
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10853-017-1191-6)
-
103
Antibacterial polyacrylonitrile nanofibers produced by alkaline hydrolysis and chlorination
Aksoy, O. E., Ates, B., & Cerkez, I. (2017). Antibacterial polyacrylonitrile nanofibers produced by alkaline hydrolysis and chlorination. Journal of Materials Science, 52(17), 10013–10022. doi:10.1007/s10853-017-1240-1
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10853-017-1240-1)
-
104
Effects of pre-and post-electrospinning plasma treatments on electrospun PCL nanofibers to improve cell interactions
Asadian, M., Grande, S., Morent, R., Nikiforov, A., Declercq, H., & De Geyter, N. (2017). Effects of pre- and post-electrospinning plasma treatments on electrospun PCL nanofibers to improve cell interactions. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 841, 012018. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/841/1/012018
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/841/1/012018/meta)
-
105
Filtration of juices by using electrospun pan membrane
ALTAY F?L?Z,AZIZZADEH FARZANEH, The Fifth International Symposium Frontiers in Polymer Science (POLY 2017), Seville/?SPANYA, 17 May?s 2017
(https://akademi.itu.edu.tr/search-results?st=PAN%20polymer)
-
106
Fundamental Investigation of PhotoActive Materials From Small Molecules to Materials
Livshits, M. (2017). Fundamental Investigation of PhotoActive Materials From Small Molecules to Materials. (Electronic Thesis or Dissertation). Retrieved from https://etd.ohiolink.edu/
(https://etd.ohiolink.edu/pg_10?0::NO:10:P10_ACCESSION_NUM:ohiou1490713190973503)
-
107
Hydrophobic coating of surfaces by plasma polymerization in an RF plasma reactor with an outer planar electrode: synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility
KARAMAN, M., G?RSOY, M., AYK?L, F., TOSUN, Z., KARS, M. D., & YILDIZ, H. B. (2017). Hydrophobic coating of surfaces by plasma polymerization in an RF plasma reactor with an outer planar electrode: synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility. Plasma Science and Technology, 19(8), 085503. doi:10.1088/2058-6272/aa6fec
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2058-6272/aa6fec/meta)
-
108
Mechanical properties and fatigue analysis on poly(ε- caprolactone)-polydopamine-coated nanofibers and poly(ε- caprolactone)-carbon nanotube composite scaffolds
Fernández, J., Auzmendi, O., Amestoy, H., Diez-Torre, A., & Sarasua, J.-R. (2017). Mechanical properties and fatigue analysis on poly(ε-caprolactone)-polydopamine-coated nanofibers and poly(ε-caprolactone)-carbon nanotube composite scaffolds. European Polymer Journal, 94, 208–221. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.07.013
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014305717302999)
-
109
Evaluation of three-layered doxycycline-collagen loaded nanofiber wound dressing
Tort, S., Acartürk, F., & Be?ikci, A. (2017). Evaluation of three-layered doxycycline-collagen loaded nanofiber wound dressing. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 529(1-2), 642–653. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.07.027
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378517317306269)
-
110
Anisotropic microfibrous scaffolds enhance the organization and function of cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells
Wanjare, M., Hou, L., Nakayama, K. H., Kim, J. J., Mezak, N. P., Abilez, O. J., … Huang, N. F. (2017). Anisotropic microfibrous scaffolds enhance the organization and function of cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials Science, 5(8), 1567–1578. doi:10.1039/c7bm00323d
(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2017/bm/c7bm00323d/unauth#!divAbstract)
-
111
Thermoresponsive Cellulose Acetate?Poly(N‐isopropylacrylamide) Core?Shell Fibers for Controlled Capture and Release of Moisture
Thakur, N., Sargur Ranganath, A., Sopiha, K., & Baji, A. (2017). Thermoresponsive Cellulose Acetate–Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Core–Shell Fibers for Controlled Capture and Release of Moisture. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9(34), 29224–29233. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b07559
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.7b07559 )
-
112
Microfibrous scaffolds enhance endothelial differentiation and organization of induced pluripotent stem cells
Kim, J. J., Hou, L., Yang, G., Mezak, N. P., Wanjare, M., Joubert, L. M., & Huang, N. F. (2017). Microfibrous Scaffolds Enhance Endothelial Differentiation and Organization of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering, 10(5), 417–432. doi:10.1007/s12195-017-0502-y
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12195-017-0502-y)
-
113
Atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment of poly-ε-caprolactone polymer solutions to improve electrospinning
Grande, S., Van Guyse, J., Nikiforov, A. Y., Onyshchenko, I., Asadian, M., Morent, R., … De Geyter, N. (2017). Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Treatment of Poly-ε-caprolactone Polymer Solutions To Improve Electrospinning. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9(38), 33080–33090. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b08439
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.7b08439)
-
114
Sugar-cane bagasse derived cellulose enhances performance of polylactide and polydioxanone electrospun scaffold for tissue engineering
Ramphul, H., Bhaw-Luximon, A., & Jhurry, D. (2017). Sugar-cane bagasse derived cellulose enhances performance of polylactide and polydioxanone electrospun scaffold for tissue engineering. Carbohydrate Polymers, 178, 238–250. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.09.046
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0144861717310718)
-
115
Thermoresponsive electrospun fibers for water harvesting applications
Thakur, N., Baji, A., & Ranganath, A. S. (2018). Thermoresponsive electrospun fibers for water harvesting applications. Applied Surface Science, 433, 1018–1024. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.113
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169433217330593)
-
116
Effects of a Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Treatment on Chitosan/Polyethylene Oxide Nanofibers and Their Cellular Interactions
Asadian, M., Onyshchenko, I., Thukkaram, M., Esbah Tabaei, P. S., Van Guyse, J., Cools, P., … De Geyter, N. (2018). Effects of a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) treatment on chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers and their cellular interactions. Carbohydrate Polymers. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.092
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0144861718310002)
-
117
Effects of plasma treatment on the surface chemistry, wettability, and cellular interactions of nanofibrous Scaffolds
Asadian, M., Declercq, H., Cornelissen, M., Morent, R., & De Geyter, N. (2017). Effects of plasma treatment on the surface chemistry, wettability, and cellular interactions of nanofibrous Scaffolds. In 31st International conference on surface modification technologies. (https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/8532609/file/8532610)
-
118
Electrospinning: A versatile processing technology for producing nanofibrous materials for biomedical and tissue-engineering applications
Senthamizhan, A., Balusamy, B., & Uyar, T. (2017). Electrospinning: A versatile processing technology for producing nanofibrous materials for biomedical and tissue-engineering applications. In Electrospun Materials for Tissue Engineering and Biomedical Applications (pp. 3-41). Woodhead Publishing.
(https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-101022-8.00001-6)
-
119
Solution electrospinning of nanofibers
Salas, C. (2017). Solution electrospinning of nanofibers. In Electrospun Nanofibers (pp. 73-108). Woodhead Publishing.
(http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100907-9.00004-0)
-
120
Microesferas magne?ticas de polifluoruro de vinilideno para estimulacio?n celular in vitro. Determinacio?n y control de los para?metros del proceso de fabricacio?n
CH?LIZ SANZ, SOF?A. (2017). Microesferas magnéticas de polifluoruro de vinilideno para estimulación celular in vitro. Determinación y control de los parámetros del proceso de fabricación.
(https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/89154)
-
121
Preparation of electrospun polyurethane nanofiber mats for the release of doxorubicine
Kili?, E., Yakar, A., & Bayramgil, N. P. (2018). Preparation of electrospun polyurethane nanofiber mats for the release of doxorubicine. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 29(1), 8.
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10856-017-6013-5)
-
122
Production and characterization of electrospun fish sarcoplasmic protein based nanofibers
Sahin, Y. M., Su, S., Ozbek, B., Yücel, S., Pinar, O., Kazan, D., … & Gunduz, O. (2018). Production and characterization of electrospun fish sarcoplasmic protein based nanofibers. Journal of food engineering, 222, 54-62.
(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.11.013)
-
123
Production of the novel fibrous structure of poly(ε-caprolactone)/tri-calcium phosphate/hexagonal boron nitride composites for bone tissue engineering
Ozbek, B., Erdogan, B., Ekren, N., Oktar, F. N., Akyol, S., Ben-Nissan, B., … & Ozen, G. (2018). Production of the novel fibrous structure of poly (ε-caprolactone)/tri-calcium phosphate/hexagonal boron nitride composites for bone tissue engineering. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 54(2), 251-260.
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41779-017-0149-0)
-
124
Raising Nanofiber Output- The Progress, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Reasons for the Pursuit
Akampumuza, O., Gao, H., Zhang, H., Wu, D., & Qin, X. H. (2018). Raising nanofiber output: the progress, mechanisms, challenges, and reasons for the pursuit. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 303(1), 1700269. (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mame.201700269)
-
125
Electrospun Janus Membrane for Efficient and Switchable Oil–Water Separation
Ranganath, A. S., & Baji, A. (2018). Electrospun Janus Membrane for Efficient and Switchable Oil–Water Separation. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 303(11), 1800272.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mame.201800272)
-
126
Anti-corrosion coating for magnesium alloys- electrospun superhydrophobic polystyrene/SiO2 composite fibers
Polat, N. H., Kap, ?., & Farzaneh, A. (2018). Anticorrosion coating for magnesium alloys: electrospun superhydrophobic polystyrene/SiO $ _ {2} $ composite fibers. Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 42(3), 672-683.
(https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/tbtkchem/issue/45567/572684)
-
127
A comparative study of electrospinning process for two different collectors- The effect of the collecting method on the nanofiber diameters
?AVDAR, F. Y., & U?UZ, A. (2019). A comparative study of electrospinning process for two different collectors: The effect of the collecting method on the nanofiber diameters. Mechanical Engineering Journal, 6(1), 18-00298.
(https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/mej/6/1/6_18-00298/_article/-char/ja/)
-
128
A comparative study of single-needle and coaxial electrospun amyloid-like protein nanofibers to investigate hydrophilic drug release behavior
Kabay, G., Demirci, C., Can, G. K., Meydan, A. E., Da?an, B. G., & Mutlu, M. (2018). A comparative study of single-needle and coaxial electrospun amyloid-like protein nanofibers to investigate hydrophilic drug release behavior. International journal of biological macromolecules, 114, 989-997.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141813018301107)
-
129
A review of low density porous materials used in laser plasma experiments
Nagai, K., Musgrave, C. S., & Nazarov, W. (2018). A review of low density porous materials used in laser plasma experiments. Physics of Plasmas, 25(3), 030501.
(https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/1.5009689)
-
130
Antibacterial Properties of PLGA Electrospun Scaffolds Containing Ciprofloxacin Incorporated by Blending or Physisorption
Buck, E., Maisuria, V., Tufenkji, N., & Cerruti, M. (2018). Antibacterial Properties of PLGA Electrospun Scaffolds Containing Ciprofloxacin Incorporated by Blending or Physisorption. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 1(3), 627-635.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsabm.8b00112)
-
131
Bioactive glass/hydroxyapatite- containing electrospun poly (ε-Caprolactone) composite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering
Deliormanl?, A. M., & Konyal?, R. (2019). Bioactive glass/hydroxyapatite-containing electrospun poly (ε-Caprolactone) composite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 55(1), 247-256.
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41779-018-0229-9)
-
132
Core–Shell Hybrid Nanowires with Protein Enabling Fast Ion Conduction for High‐Performance Composite Polymer Electrolytes
Fu, X., Wang, Y., Fan, X., Scudiero, L., & Zhong, W. H. (2018). Core–Shell Hybrid Nanowires with Protein Enabling Fast Ion Conduction for High‐Performance Composite Polymer Electrolytes. Small, 14(49), 1803564.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/smll.201803564)
-
133
Design and development of pH-responsive polyurethane membranes for intravaginal release of nanomedicines
Kim, S., Traore, Y. L., Ho, E. A., Shafiq, M., Kim, S. H., & Liu, S. (2018). Design and development of pH-responsive polyurethane membranes for intravaginal release of nanomedicines. Acta biomaterialia, 82, 12-23.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1742706118305932)
-
134
Development and characterization of methylprednisolone loaded delayed release nanofibers
Turanl?, Y., Tort, S., & Acartürk, F. (2019). Development and characterization of methylprednisolone loaded delayed release nanofibers. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 49, 58-65.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1773224718307780)
-
135
Development of Carbon Nanofiber Yarns by Electrospinning
Demir, A., Acikabak, B., & Ahan, Z. (2018, December). Development of Carbon Nanofiber Yarns by Electrospinning. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 460, No. 1, p. 012027). IOP Publishing.
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/460/1/012027/meta)
-
136
Effect of heat treatment conditions on magnesium borate fibers prepared via electrospinning
Storti, E., Jankovsk?, O., Colombo, P., & Aneziris, C. G. (2018). Effect of heat treatment conditions on magnesium borate fibers prepared via electrospinning. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 38(11), 4109-4117.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0955221918302632)
-
137
Effect of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/chitosan (CS) blend ratios on morphological, optical and thermal properties of electrospun nanofibers
A?IK, G., Kamaci, M., ?ZATA, B., & CANSOY, C. E. ?. (2019). Effect of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan blend ratios on morphological, optical, and thermal properties of electrospun nanofibers. Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 43(1), 137-149.
(https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/tbtkchem/issue/45572/572771)
-
138
Effect of temperature, viscosity and surface tension on gelatine structures produced by modified 3D printer
Kalkandelen, C., Ozbek, B., Ergul, N. M., Akyol, S., Moukbil, Y., Oktar, F. N., … & Gunduz, O. (2017, December). Effect of temperature, viscosity and surface tension on gelatine structures produced by modified 3D printer. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 293, No. 1, p. 012001). IOP Publishing.
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/293/1/012001/meta)
-
139
Effects of Polymethylsilsesquioxane concentration on morphology shape of electrosprayed particles
Unal, S., Oktar, F. N., & Gunduz, O. (2018). Effects of Polymethylsilsesquioxane concentration on morphology shape of electrosprayed particles. Materials Letters, 221, 107-110.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167577X18304786)
-
140
Electrospinning for membrane fabrication- Strategies and applications
Tijing, L. D., Woo, Y. C., Yao, M., Ren, J., & Shon, H. K. (2017). 1.16 Electrospinning for Membrane Fabrication: Strategies and Applications. Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering, 418–444. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-409547-2.12262-0
(https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313668516_Electrospinning_for_Membrane_Fabrication_Strategies_and_Applications)
-
141
Electrospinning of tri-acetyl-β-cyclodextrin (TA-β-CD) functionalized low-density polyethylene to minimize sulfur odor volatile compounds
Shin, J., Lee, E. J., & Ahn, D. U. (2018). Electrospinning of tri-acetyl-β-cyclodextrin (TA-β-CD) functionalized low-density polyethylene to minimize sulfur odor volatile compounds. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 18, 107-114.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214289418302448)
-
142
Electrospun polystyrene fibers knitted around imprinted acrylate microspheres as sorbent for paraben derivatives
Demirkurt, M., Olcer, Y. A., Demir, M. M., & Eroglu, A. E. (2018). Electrospun polystyrene fibers knitted around imprinted acrylate microspheres as sorbent for paraben derivatives. Analytica chimica acta, 1014, 1-9.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003267018302058)
-
143
Encapsulation of indocyanine green in poly(lactic acid) nanofibers for using as a nanoprobe in biomedical diagnostics
Ege, Z. R., Akan, A., Oktar, F. N., Lin, C. C., Karademir, B., & Gunduz, O. (2018). Encapsulation of indocyanine green in poly (lactic acid) nanofibers for using as a nanoprobe in biomedical diagnostics. Materials Letters, 228, 148-151.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167577X18309133)
-
144
Fabrication of electrospun poly(ethylene terephthalate) scaffolds: Characterization and their potential on cell proliferation in vitro
D?ZYER, ?. (2017). FABRICATION OF ELECTROSPUN POLY (ETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE) SCAFFOLDS: CHARACTERIZATION AND THEIR POTENTIAL ON CELL PROLIFERATION IN VITRO. TEKST?L VE KONFEKS?YON, 27(4), 334-341.
(https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/tekstilvekonfeksiyon/issue/33462/372022)
-
145
Fabrication of Antibacterial Polyvinylalcohol Nanocomposite Mats with Soluble Starch Coated Silver Nanoparticles
Aktürk, A., Taygun, M. E., Güler, F. K., Goller, G., & Kü?ükbayrak, S. (2019). Fabrication of antibacterial polyvinylalcohol nanocomposite mats with soluble starch coated silver nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 562, 255-262.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0927775718310252)
-
146
Fabrication of PEOT/PBT Nanofibers by Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Treatment of Electrospinning Solutions for Tissue Engineering
Grande, S., Cools, P., Asadian, M., Van Guyse, J., Onyshchenko, I., Declercq, H., … & De Geyter, N. (2018). Fabrication of PEOT/PBT nanofibers by atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment of electrospinning solutions for tissue engineering. Macromolecular Bioscience, 18(12), 1800309.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mabi.201800309)
-
147
Highly Hydrophobic Electrospun Reduced Graphene Oxide/Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) Membranes for Use in Membrane Distillation
Chen, T., Soroush, A., & Rahaman, M. S. (2018). Highly Hydrophobic Electrospun Reduced Graphene Oxide/Poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) Membranes for Use in Membrane Distillation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 57(43), 14535-14543.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b03584)
-
148
Interfacial Polymerization with Electrosprayed Microdroplets- Toward Controllable and Ultrathin Polyamide Membranes
Ma, X. H., Yang, Z., Yao, Z. K., Guo, H., Xu, Z. L., & Tang, C. Y. (2018). Interfacial polymerization with electrosprayed microdroplets: Toward controllable and ultrathin polyamide membranes. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 5(2), 117-122.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.estlett.7b00566)
-
149
Investigation of plasma‐induced chemistry in organic solutions for enhanced electrospun PLA nanofibers
Rezaei, F., Gorbanev, Y., Chys, M., Nikiforov, A., Van Hulle, S. W., Cos, P., … & De Geyter, N. (2018). Investigation of plasma‐induced chemistry in organic solutions for enhanced electrospun PLA nanofibers. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 15(6), 1700226.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ppap.201700226)
-
150
Levan based fibrous scaffolds electrospun via co-axial and single-needle techniques for tissue engineering applications
Avsar, G., Agirbasli, D., Agirbasli, M. A., Gunduz, O., & Oner, E. T. (2018). Levan based fibrous scaffolds electrospun via co-axial and single-needle techniques for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydrate polymers, 193, 316-325.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0144861718303382)
-
151
Micro-Nanofibrillar Polycaprolactone Scaffolds as Translatable Osteoconductive Grafts for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Defects without Infection
Ghannadian, P., Moxley Jr, J. W., Machado de Paula, M. M., Lobo, A. O., & Webster, T. J. (2018). Micro-Nanofibrillar Polycaprolactone Scaffolds as Translatable Osteoconductive Grafts for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Defects without Infection. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 1(5), 1566-1578.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsabm.8b00453)
-
152
Modification of electrospun PVA/PAA scaffolds by cold atmospheric plasma- alignment, antibacterial activity, and biocompatibility
Arik, N., Inan, A., Ibis, F., Demirci, E. A., Karaman, O., Ercan, U. K., & Horzum, N. (2019). Modification of electrospun PVA/PAA scaffolds by cold atmospheric plasma: alignment, antibacterial activity, and biocompatibility. Polymer Bulletin, 76(2), 797-812.
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00289-018-2409-8)
-
153
Morphological and Mechanical Characterization of Electrospun Polylactic Acid and Microcrystalline Cellulose
Gaitán, A., & Gacitúa, W. (2018). Morphological and mechanical characterization of electrospun polylactic acid and microcrystalline cellulose. BioResources, 13(2), 3659-3673.
(https://ojs.cnr.ncsu.edu/index.php/BioRes/article/view/BioRes_13_2_3659_Gaitan_Morphological_Mechanical_Electrospun_Cellulose)
-
154
Nanofibered Gelatin‐Based Nonwoven Elasticity Promotes Epithelial Histogenesis
Jedrusik, N., Meyen, C., Finkenzeller, G., Stark, G. B., Meskath, S., Schulz, S. D., … & Tomakidi, P. (2018). Nanofibered Gelatin‐Based Nonwoven Elasticity Promotes Epithelial Histogenesis. Advanced healthcare materials, 7(10), 1700895.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adhm.201700895)
-
155
PA6 nanofibre production: A comparison between rotary jet spinning and electrospinning
Rogalski, J., Bastiaansen, C., & Peijs, T. (2018). PA6 nanofibre production: A comparison between rotary jet spinning and electrospinning. Fibers, 6(2), 37.
(https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6439/6/2/37)
-
156
Patent - US20180142379A1 - Electrospinning of fluoropolymers
Poss, A. J., Nalewajek, D., Cantlon, C. L., Lu, C., & Wo, S. (2018). U.S. Patent Application No. 15/802,673.
(https://patents.google.com/patent/US20180142379A1/en)
-
157
Patent - US20180215882A1 - Swellable and insoluble nanofibers and use thereof in the treatment of essentially aqueous effluents
Viel, P., Benzaqui, M., & Shilova, E. (2018). U.S. Patent Application No. 15/750,044.
(https://patents.google.com/patent/US20180215882A1/en)
-
158
Patent - US20180301690A1 - Metal oxide nanofiber electrode and method
Ozkan, C. S., Ozkan, M., Bell, J., & Ye, R. (2018). U.S. Patent Application No. 15/776,720. (https://patents.google.com/patent/US20180301690A1/en)
-
159
Plasma Modification of Poly Lactic Acid Solutions to Generate High Quality Electrospun PLA Nanofibers
Rezaei, F., Nikiforov, A., Morent, R., & De Geyter, N. (2018). Plasma modification of poly lactic acid solutions to generate high quality electrospun PLA nanofibers. Scientific reports, 8(1), 2241.
(https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-20714-5)
-
160
Polivinil alkol kompozit nanoliflerin haz?rlanmas? ve kat?-faz polivinil alkol'u?n fotokatalitik bozunmas?
K?ysüren, H. N., & K?ysüren, ?. (2018). Polivinil alkol kompozit nanoliflerin haz?rlanmas? ve kat?-faz polivinil alkolün fotokatalitik bozunmas?. Journal of the Faculty of Engineering & Architecture of Gazi University, 33(4).
(https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/601784)
-
161
Polymeric and metal oxide structured nanofibrous composites fabricated by electrospinning as highly efficient hydrogen evolution catalyst
Figen, A. K., & Filiz, B. C. (2019). Polymeric and metal oxide structured nanofibrous composites fabricated by electrospinning as highly efficient hydrogen evolution catalyst. Journal of colloid and interface science, 533, 82-94.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021979718309639)
-
162
Preparation and mineralization of 13-93 bioactive glass-containing electrospun poly-epsilon-caprolactone composite nanofibrous mats
Konyal?, R., & Deliormanl?, A. M. (2019). Preparation and mineralization of 13-93 bioactive glass-containing electrospun poly-epsilon-caprolactone composite nanofibrous mats. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 32(5), 690-709.
(https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0892705718772889)
-
163
Salinomycin-loaded Nanofibers for Glioblastoma Therapy
Norouzi, M., Abdali, Z., Liu, S., & Miller, D. W. (2018). Salinomycin-loaded Nanofibers for Glioblastoma Therapy. Scientific reports, 8(1), 9377.
(https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-27733-2)
-
164
Spunbond Dokusuz Tekstil Yu?zeyi U?zerine Elektro C?ekim Yo?ntemi ile Nano Boyutta Grafen Kaplanmas? ve Karakterizasyonu
ALMA, M. H., YAZICI, M., YILDIRIM, B., & T?YEK, ?. (2017). Spunbond Dokusuz Tekstil Yüzeyi ?zerine Elektro ?ekim Y?ntemi ile Nano Boyutta Grafen Kaplanmas? ve Karakterizasyonu. Tekstil ve Mühendis, 24(108), 243-253.
(https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/teksmuh/issue/33861/374969)
-
165
Superhydrophobic EVA copolymer fibers- the impact of chemical composition on wettability and photophysical properties
Acik, G., Kamaci, M., & Cansoy, C. E. (2018). Superhydrophobic EVA copolymer fibers: the impact of chemical composition on wettability and photophysical properties. Colloid and Polymer Science, 296(11), 1759-1766.
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00396-018-4395-7)
-
166
The investigation of the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of multi-layered nanocomposite materials from reduced graphene oxide-doped P(AN-VAc) nanofiber mats/PP spunbond
Tiyek, ?., Yaz?c?, M., Alma, M. H., & Karata?, ?. (2019). The investigation of the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of multi-layered nanocomposite materials from reduced graphene oxide-doped P (AN-VAc) nanofiber mats/PP spunbond. Journal of Composite Materials, 53(11), 1541-1553.
(https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0021998318806973)
-
167
The uniaxial and coaxial encapsulations of sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) concentrate by electrospinning and their in vitro bioaccessibility
Isik, B. S., Altay, F., & Capanoglu, E. (2018). The uniaxial and coaxial encapsulations of sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) concentrate by electrospinning and their in vitro bioaccessibility. Food chemistry, 265, 260-273.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814618308719)
-
168
Thermal Conductivity of Electrospun Polyethylene Nanofibers
Ma, J., Zhang, Q., Mayo, A., Ni, Z., Yi, H., Chen, Y., … & Li, D. (2015). Thermal conductivity of electrospun polyethylene nanofibers. Nanoscale, 7(40), 16899-16908.
(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/nr/c5nr04995d/unauth#!divAbstract)
-
169
Bacteria-triggered release of a potent biocide from core-shell polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-based nanofibers for wound dressing application
Li, W. (2018). Bacteria-triggered release of a potent biocide from core-shell polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-based nanofibers for wound dressing application.
(https://mspace.lib.umanitoba.ca/handle/1993/33473)
-
170
Studium kinetiky funkcionalizace povrchu nanovla?ken po aktivaci plazmatem
R??ek, V. (2018). Studium kinetiky funkcionalizace povrchu nanovláken po aktivaci plazmatem.
(https://dspace.tul.cz/handle/15240/32257)
-
171
Using Of Nanofiber Based Electrodes For Detection Of Organic Molecules
Ma?hemut?, A. (2018). Using Of Nanofiber Based Electrodes For Detection Of Organic Molecules (Master’s thesis, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü).
(http://www.openaccess.hacettepe.edu.tr:8080/xmlui/handle/11655/4603)
-
172
Wide-ranging diameter scale of random and highly aligned PCL fibers electrospun using controlled working parameters
Ghobeira, R., Asadian, M., Vercruysse, C., Declercq, H., De Geyter, N., & Morent, R. (2018). Wide-ranging diameter scale of random and highly aligned PCL fibers electrospun using controlled working parameters. Polymer, 157, 19-31.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032386118309455)
-
173
A comparative study on pre- and post-production plasma treatments of PCL films and nanofibers for improved cell-material interactions
Asadian, M., Grande, S., Onyshchenko, I., Morent, R., Declercq, H., & De Geyter, N. (2019). A comparative study on pre-and post-production plasma treatments of PCL films and nanofibers for improved cell-material interactions. Applied Surface Science, 481, 1554-1565.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169433219308554)
-
174
Bacteria-Responsive Single and Core–Shell Nanofibrous Membranes Based on Polycaprolactone/Poly(ethylene succinate) for On-Demand Release of Biocides
Abdali, Z., Logsetty, S., & Liu, S. (2019). Bacteria-Responsive Single and Core–Shell Nanofibrous Membranes Based on Polycaprolactone/Poly (ethylene succinate) for On-Demand Release of Biocides. ACS Omega, 4(2), 4063-4070.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsomega.8b03137)
-
175
Biocompatibility of Cyclopropylamine-Based Plasma Polymers Deposited at Sub-Atmospheric Pressure on Poly (ε-caprolactone) Nanofiber Meshes
Chan, K. V., Asadian, M., Onyshchenko, I., Declercq, H., Morent, R., & De Geyter, N. (2019). Biocompatibility of Cyclopropylamine-Based Plasma Polymers Deposited at Sub-Atmospheric Pressure on Poly (ε-caprolactone) Nanofiber Meshes. Nanomaterials, 9(9), 1215.
(https://www.mdpi.com/2079-4991/9/9/1215)
-
176
Bioinspired scaffold induced regeneration of neural tissue
Altun, E., Aydogdu, M. O., Togay, S. O., Sengil, A. Z., Ekren, N., Haskoylu, M. E., … & Ahmed, J. (2019). Bioinspired scaffold induced regeneration of neural tissue. European Polymer Journal, 114, 98-108.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014305718324765)
-
177
Biomimetic hybrid scaffold consisting of co-electrospun collagen and PLLCL for 3D cell culture
Türker, E., Yildiz, ?. H., & Yildiz, A. A. (2019). Biomimetic hybrid scaffold consisting of co-electrospun collagen and PLLCL for 3D cell culture. International journal of biological macromolecules.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141813019350019)
-
178
Development of TiO2 nanofibers based semiconducting humidity sensor- adsorption kinetics and DFT computations
Farzaneh, A., Esrafili, M. D., & Mermer, ?. (2019). Development of TiO2 nanofibers based semiconducting humidity sensor: adsorption kinetics and DFT computations. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 121981.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0254058419307801)
-
179
Diatom shell incorporated PHBV/PCL-pullulan co-electrospun scaffold for bone tissue engineering
Dalgic, A. D., Atila, D., Karatas, A., Tezcaner, A., & Keskin, D. (2019). Diatom shell incorporated PHBV/PCL-pullulan co-electrospun scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 100, 735-746.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493118326286)
-
180
Dual effective core-shell electrospun scaffolds- Promoting osteoblast maturation and reducing bacteria activity
De-Paula, M. M. M., Afewerki, S., Viana, B. C., Webster, T. J., Lobo, A. O., & Marciano, F. R. (2019). Dual effective core-shell electrospun scaffolds: Promoting osteoblast maturation and reducing bacteria activity. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 103, 109778.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493118309032)
-
181
Effects of UV Exposure Time on Nanofiber Wound Dressing Properties During Sterilization
Tort, S., Demir?z, F. T., Y?ld?z, S., & Acartürk, F. (2019). Effects of UV exposure time on nanofiber wound dressing properties during sterilization. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation, 1-8.
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12247-019-09383-7)
-
182
Electron Microscopy Investigation of CeO2 Nanofibers Supported Noble Metal (Pt, Pd and Ru) Catalysts for CO Oxidation
Liu, Z., Lu, Y., Li, J., Wang, Y., Wujcik, E. K., & Wang, R. (2019). Electron Microscopy Investigation of CeO 2 Nanofibers Supported Noble Metal (Pt, Pd and Ru) Catalysts for CO Oxidation. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 25(S2), 2176-2177.
(https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927619011619)
-
183
Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers- Methods, Materials, and Applications
Xue, J., Wu, T., Dai, Y., & Xia, Y. (2019). Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chemical reviews, 119(8), 5298-5415.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00593)
-
184
Electrospinning- The Setup and Procedure
Long, Y. Z., Yan, X., Wang, X. X., Zhang, J., & Yu, M. (2019). Electrospinning: The Setup and Procedure. In Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications (pp. 21-52). William Andrew Publishing.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323512701000029)
-
185
Electrospray Deposition of Discrete Nanoparticles- Studies on Pulsed-Field Electrospray and Analytical Applications
Kremer, M. H. (2019). Electrospray Deposition of Discrete Nanoparticles: Studies on Pulsed-Field Electrospray and Analytical Applications.
(https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/concern/graduate_thesis_or_dissertations/9p290g61r)
-
186
Electrospun Fibers of Polyester, with Both Nano- and Micron Diameters, Loaded with Antioxidant for Application as Wound Dressing or Tissue Engineered Scaffolds
Ferna?ndez, J., Ruiz-Ruiz, M., & Sarasua, J. R. (2019). Electrospun Fibers of Polyester, with Both Nano-and Micron Diameters, Loaded with Antioxidant for Application as Wound Dressing or Tissue Engineered Scaffolds. ACS Applied Polymer Materials.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsapm.9b00108)
-
187
Encapsulated melatonin in polycaprolactone (PCL) microparticles as a promising graft material
Gurler, E. B., Ergul, N. M., Ozbek, B., Ekren, N., Oktar, F. N., Haskoylu, M. E., … & Temiz, A. F. (2019). Encapsulated melatonin in polycaprolactone (PCL) microparticles as a promising graft material. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 100, 798-808.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493118329187)
-
188
Examination of novel electrosprayed biogenic hydroxyapatite coatings on Si3N4 and Si3N4 /MWCNT ceramic composite
Zagyva, T., Balázsi, K., & Balázsi, C. (2019). Examination of novel electrosprayed biogenic hydroxyapatite coatings on Si3N4 and Si3N4/MWCNT ceramic composite. PROCESSING AND APPLICATION OF CERAMICS, 13(2), 132-138.
(http://www.doiserbia.nb.rs/Article.aspx?ID=1820-61311902132Z#.XXKXgJMzbfY)
-
189
Fabrication of dual-functional composite yarns with a nanofibrous envelope using high throughput AC needleless and collectorless electrospinning
Valtera, J., Kalous, T., Pokorny, P., Batka, O., Bilek, M., Chvojka, J., … & Beran, J. (2019). Fabrication of dual-functional composite yarns with a nanofibrous envelope using high throughput AC needleless and collectorless electrospinning. Scientific reports, 9(1), 1801. (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-38557-z)
-
190
Flexible S/DPAN/KB Nanofiber Composite as Binder-Free Cathodes for Li-S Batteries
Kalybekkyzy, S., Mentbayeva, A., Kahraman, M. V., Zhang, Y., & Bakenov, Z. (2019). Flexible S/DPAN/KB Nanofiber Composite as Binder-Free Cathodes for Li-S Batteries. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 166(3), A5396-A5402. (http://jes.ecsdl.org/content/166/3/A5396.short)
-
191
Hydrogen production from sodium borohydride originated compounds- Fabrication of electrospun nano-crystalline Co3O4 catalyst and its activity
Filiz, B. C., & Figen, A. K. (2019). Hydrogen production from sodium borohydride originated compounds: Fabrication of electrospun nano-crystalline Co3O4 catalyst and its activity. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(20), 9883-9895. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360319919306974)
-
192
Improved catalytic performance of metal oxide catalysts fabricated with electrospinning in ammonia borane methanolysis for hydrogen production
Figen, A. K. (2019). Improved catalytic performance of metal oxide catalysts fabricated with electrospinning in ammonia borane methanolysis for hydrogen production. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360319919305610)
-
193
Improved Multicellular Response, Biomimetic Mineralization, Angiogenesis, and Reduced Foreign Body Response of Modified Polydioxanone Scaffolds for Skeletal Tissue Regeneration
Goonoo, N., Fahmi, A., Jonas, U., Gimié, F., Arsa, I. A., Bénard, S., … & Bhaw-Luximon, A. (2019). Improved Multicellular Response, Biomimetic Mineralization, Angiogenesis, and Reduced Foreign Body Response of Modified Polydioxanone Scaffolds for Skeletal Tissue Regeneration. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 11(6), 5834-5850. (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.8b19929)
-
194
Improvement of carbon nanotube dispersion in electrospun polyacrylonitrile fiber through plasma surface modification
Gürsoy, M., ?zcan, F., & Karaman, M. (2019). Improvement of carbon nanotube dispersion in electrospun polyacrylonitrile fiber through plasma surface modification. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 136(31), 47768.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/app.47768)
-
195
Kinetics and Isotherms Studies of the Adsorption of Hg(II) onto Iron Modified Montmorillonite/Polycaprolactone Nanofiber Membrane
Somera, L. R., Cuazon, R., Cruz, J. K., & Diaz, L. J. (2019, May). Kinetics and Isotherms Studies of the Adsorption of Hg (II) onto Iron Modified Montmorillonite/Polycaprolactone Nanofiber Membrane. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 540, No. 1, p. 012005). IOP Publishing.
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/540/1/012005/meta)
-
196
Latest Progress in Electrospun Nanofibers for Wound Healing Applications
Memic, A., Abudula, T., Mohammed, H. S., Joshi Navare, K., Colombani, T., & Bencherif, S. A. (2019). Latest progress in electrospun nanofibers for wound healing applications. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2(3), 952-969.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsabm.8b00637)
-
197
Lipase-Responsive Electrospun Theranostic Wound Dressing for Simultaneous Recognition and Treatment of Wound Infection
Singh, H., Li, W., Kazemian, M. R., Yang, R., Yang, C., Logsetty, S., & Liu, S. (2019). Lipase-Responsive Electrospun Theranostic Wound Dressing for Simultaneous Recognition and Treatment of Wound Infection. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2(5), 2028-2036.
(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsabm.9b00076)
-
198
Needle-less Electrospinning
Yan, G., Niu, H., & Lin, T. (2019). Needle-less Electrospinning. In Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications (pp. 219-247). William Andrew Publishing.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323512701000078)
-
199
Novel biodegradable and non-fouling systems for controlled-release based on poly(ε-caprolactone)/Quercetin blends and biomimetic bacterial S-layer coatings
Sanchez-Rexach, E., Iturri, J., Fernandez, J., Meaurio, E., Toca-Herrera, J. L., & Sarasua, J. R. (2019). Novel biodegradable and non-fouling systems for controlled-release based on poly (ε-caprolactone)/Quercetin blends and biomimetic bacterial S-layer coatings. RSC Advances, 9(42), 24154-24163.
(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/ra/2019/c9ra04398e#!divAbstract)
-
200
On the detailed mechanical response investigation of PHBV/PCL and PHBV/PLGA electrospun mats
Bal, B., Tugluca, I. B., Koc, N., & Isoglu, I. A. (2019). On the detailed mechanical response investigation of PHBV/PCL and PHBV/PLGA electrospun mats. Materials Research Express, 6(6), 065411.
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2053-1591/ab0eaa/meta)
-
201
Patent - US10197498B2 - Compositions and methods for measurement of analytes
Ruckh, T. T., Balaconis, M. K., Clark, H. A., & Skipwith, C. (2019). U.S. Patent Application No. 10/197,498.
(https://patents.google.com/patent/US10197498B2/en?oq=US10197498B2+)
-
202
Patent - US10211449B2 - Battery electrode and method
Ozkan, C. S., Ozkan, M., & Favors, Z. (2019). U.S. Patent Application No. 10/211,449. (https://patents.google.com/patent/US10211449B2/en)
-
203
Polypropylene composite hernia mesh with anti-adhesion layer composed of polycaprolactone and oxidized regenerated cellulose
Sezer, U. A., Sanko, V., Gulmez, M., Aru, B., Sayman, E., Aktekin, A., … & Sezer, S. (2019). Polypropylene composite hernia mesh with anti-adhesion layer composed of polycaprolactone and oxidized regenerated cellulose. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 99, 1141-1152.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493118327024)
-
204
Polypropylene microfibers via solution electrospinning under ambient conditions
Acik, G., & Altinkok, C. (2019). Polypropylene microfibers via solution electrospinning under ambient conditions. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 136(45), 48199.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/app.48199)
-
205
Preparation and characterization of electrospun polylactic acid/sodium alginate/orange oyster shell composite nanofiber for biomedical application
Cesur, S., Oktar, F. N., Ekren, N., Kilic, O., Alkaya, D. B., Seyhan, S. A., … & Gunduz, O. (2019). Preparation and characterization of electrospun polylactic acid/sodium alginate/orange oyster shell composite nanofiber for biomedical application. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 1-11.
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41779-019-00363-1)
-
206
Preparation of electrospun PCL-based scaffolds by mono/multi-functionalized GO
Basar, A. O., Sadhu, V., & Sasmazel, H. T. (2019). Preparation of electrospun PCL-based scaffolds by mono/multi-functionalized GO. Biomedical Materials, 14(4), 045012.
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-605X/ab2035/meta)
-
207
Proses parametreleri ve ??zelti ?zelliklerinin koaksiyal elektropüskürtme y?netemi ile elde edilen nanopartiküllerin morfolojik ?zellikleri üzerine etkisi
Mete, A. A., & Atay, E. PROSES PARAMETRELER? VE ??ZELT? ?ZELL?KLER?N?N KOAKS?YAL ELEKTROP?SK?RTME Y?NTEM? ?LE ELDE ED?LEN NANOPART?K?LLER?N MORFOLOJ?K ?ZELL?KLER? ?ZER?NE ETK?S?. GIDA, 44(3), 534-551.
(https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/gida/article/531149)
-
208
Role of rheology on the formation of Nanofibers from pectin and polyethylene oxide blends
Akinalan Balik, B., & Argin, S. (2019). Role of rheology on the formation of Nanofibers from pectin and polyethylene oxide blends. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 48294.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/app.48294)
-
209
Synergetic effect of electrospun PCL fiber size, orientation and plasma-modified surface chemistry on stem cell behavior
Ghobeira, R., Philips, C., Liefooghe, L., Verdonck, M., Asadian, M., Cools, P., … & Morent, R. (2019). Synergetic effect of electrospun PCL fiber size, orientation and plasma-modified surface chemistry on stem cell behavior. Applied Surface Science, 485, 204-221.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169433219311018)
-
210
Synthesis and characterization of calcium zirconate nanofibers produced by electrospinning
Storti, E., Himcinschi, C., Kortus, J., & Aneziris, C. G. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of calcium zirconate nanofibers produced by electrospinning. Journal of the European Ceramic Society.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0955221919305485)
-
211
Synthesis and characterization of electrospun PVA/Zn2+ metal composite nanofibers for lipase immobilization with effective thermal, pH stabilities and reusability
I?ik, C., Arabaci, G., Do?a?, Y. I., Deveci, ?., & Teke, M. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of electrospun PVA/Zn2+ metal composite nanofibers for lipase immobilization with effective thermal, pH stabilities and reusability. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 99, 1226-1235.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493118309317)
-
212
Synthesis and mechanical properties of para‐aramid nanofibers
Trexler, M. M., Hoffman, C., Smith, D. A., Montalbano, T. J., Yeager, M. P., Trigg, D., … & Xia, Z. (2019). Synthesis and mechanical properties of para‐aramid nanofibers. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 57(10), 563-573.
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/polb.24810)
-
213
Nerve guidance conduit application of magnesium alloys
?zkan, O. (2019). NERVE GUIDANCE CONDUIT APPLICATION OF MAGNESIUM ALLOYS.
(http://www.openaccess.hacettepe.edu.tr:8080/xmlui/handle/11655/6176)
-
214
Thiolation of polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofibers by inductively coupled plasma (ICP) polymerization- Physical, chemical and biological properties
Asadian, M., Onyshchenko, I., Thiry, D., Cools, P., Declercq, H., Snyders, R., … & De Geyter, N. (2019). Thiolation of polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofibers by inductively coupled plasma (ICP) polymerization: Physical, chemical and biological properties. Applied Surface Science, 479, 942-952.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169433219305203)
-
215
Electrospun nanofibers for biomedical applications
-
216
Lamination of Separators to Electrodes using Electrospinning
Springer Bernhard Christian, Frankenberger Martin, Pettinger Karl-Heinz. PLoS One; San Francisco Vol. 15, Iss. 1, (Jan 2020): e0227903. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0227903
https://search.proquest.com/openview/a108579a31b0ed99b86e3d8f49ae9148/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1436336
-
217
Electrospinning of Y2O3- and MgO-stabilized zirconia nanofibers and characterization of the evolving phase composition and morphology during thermal treatment
Claudia Heuera, Enrico Stortia, Thomas Graule, Christos G.Aneziris.
EMPA, Eidgen?ssische Materialprüfungs- und Forschungsanstalt, Laboratory for High Performance Ceramics, ?berlandstr. 129, 8600, Dübendorf, Switzerland.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272884220302601?via%3Dihub
-
218
Measurement of impact characteristics in a string using electrospun PVDF nanofibers strain sensors
Rahul KumarSingh, Sun WohLye, JianminMiao.
School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924424719317200?via%3Dihub
-
219
Radicals and Ions Formed in Plasma-Treated Organic Solvents: A Mechanistic Investigation to Rationalize the Enhancement of Electrospinnability of Polycaprolactone
Silvia Grande, Francesco Tampieri, Anton Nikiforov, Agata Giardina, Antonio Barbon, Pieter Cools, Rino Morent, Cristina Paradisi, Ester Marotta and Nathalie De Geyter.
Research Unit Plasma Technology, Department of Applied Physics, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium/Department of Chemical Sciences, Università degli Studi di Padova, Padua, Italy.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2019.00344/full
-
220
Aging effect of atmospheric pressure plasma jet treated polycaprolactone polymer solutions on electrospinning properties
Silvia Grande,Joachim Van Guyse, Anton Y. Nikiforov, Iuliia Onyshchenko, Mahtab Asadian, Rino Morent, Richard Hoogenboom and Nathalie De Geyte.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/app.48914
-
221
Electrospinning of linezolid loaded PLGA nanofibers: effect of solvents on its spinnability, drug delivery, mechanical properties, and antibacterial activities
-
222
Halochromic composite nanofibrous mat for wound healing monitoring
Ayben Pakolpak??l, Bilgen Osman, Elif Tümay ?zer, Yasemin ?ahan, Beh?et Becerir, G?khan G?ktalay and Esra Karaca
2020 IOP Publishing Ltd
Materials Research Express, Volume 6, Number 12
-
223
Synthesis and morphology optimization of electrospun SiBNC nanofibers
Kamal Asadi-Pakdel, Rouhollah Mehdinavaz Aghdama, Mehdi Shahedi Asl and Mohammad Ali Faghihi Sani.
1化用于骨组织工程的明胶/银纳米颗粒/生物活性玻璃纳米复合材料的静电纺丝工艺变量
Aysen Akturk,Melek
Erol Taygun,Gultekin Goller伊斯坦堡技术大学科学研究项目基金会,授予/奖项编号:38881
2聚乙烯基硼酸酯/聚乙烯醇(PVB / PVA)共混纳米纤维的制备与表征
3功率和进料速率对静电纺丝法生产聚氨酯纳米纤维的影响
4 Ph响应性聚(2-二异丙基氨基)甲基丙烯酸乙酯薄膜的化学气相沉积
5.SuperSuperator纳米涂层合成的5热长丝支撑化学气相沉积法
6聚乙烯醇/碳纳米管(PVA / CNT)导电纳米纤维的制备与表征
7用于体内连续葡萄糖监测的荧光传感器的开发和设计
8不同灭菌方法对聚酯表面的影响
9聚合物纳米纤维:纳米技术的基础
10电纺明胶纳米纤维的电纺丝工艺及其表征参数
11一种新型喷嘴原型的设计,可在静电纺丝过程中提高生产率并改善涂层质量
12电纺聚乙烯基硼酸酯/聚(甲基丙烯酸甲酯)(PVB / PMMA)共混纳米纤维
13静电纺丝的工业规模化及其在聚合物纳米纤维中的应用
14模板热丝化学气相沉积法辅助合成光催化二氧化钛纳米管
15UV照明对新型聚(丙二醇)-B-聚苯乙烯嵌段共聚物制备的金属-聚合物-半导体二j管电学特性的影响
16应用功率与进料速度对聚氨酯纳米纤维生产影响的实验研究
17用于阴道抗HIV药物递送的电纺纤维
18聚乙烯基硼酸酯的合成; 静电纺丝法制备Ros纤维及表征19木质素基碳纤维的商业可行性分析
20Electrospun抗菌纳米纤维:生产,活性和体内应用
21种葡萄糖敏感的纳米纤维支架,针对生理状况具有改进的传感设计
22含有明胶或醋酸明胶纤维素的静电纺纳米纤维在番茄酱中的预防脱水收缩作用
23电纺聚乙烯纳米纤维的导热系数
用于纳米纤维聚己内酯纤维网的24氯仿-甲酸溶剂系统
25电纺45S5生物活性玻璃纳米纤维的制备和体外表征
26迈向可伸缩的wu粘结剂电j:通过电纺制SiO2纳米纤维的Mg降低,碳包覆的硅纳米纤维纸
27醋酸纤维基-聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)基的功能性表面,具有触发温度的可切换润湿性
28用于伤口敷料和组织工程的纳米纤维聚己内酯(PCL)和胶原蛋白混纺聚己内酯的静电纺丝
29膦功能化的静电纺丝聚乙烯醇/二氧化硅纳米纤维,作为去除锰和镍离子水溶液的高效吸附剂
适用于高容量和高速率锂离子电池的30站式Ni-Nio纳米纤维布阳j
31种生物激发的Pd催化剂功能化的WO3纳米管的同轴电纺丝及其异的氢感测性能
用于生物医学的32电纺铈和镓的硅酸盐基13-93生物活性玻璃纤维
33含二氧化钛的电纺聚乙烯醇/
Pluronic F127混合纳米纤维,用于抗菌伤口敷料
34电纺13–93生物活性玻璃纳米纤维的制备,体外矿化和成骨细胞反应
通过同时电纺PAN和PSU解决方案制造35种薄膜
36将纳米技术应用于石油工程脱硫工艺
37电纺聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)纳米纤维的润湿性和吸湿性研究
38通过静电纺丝制备聚己内酯纳米纤维网的替代溶剂系统
39同轴静电纺丝聚己内酯纳米纤维对亲水性药物的控制释放
40在制备非晶态药物剂型的微纳米加工技术中的新进展
41电纺纳米纤维催化剂的制备与氨硼烷的释氢效率
42使用PVDF颗粒增强电纺PAN纳米纤维膜的机械和物理性能
43扩大生命周期清单框架的建议:磷酸锂铁阴j应用纳米纤维的案例
44电纺微分润湿膜,有效分离油水
45关于分层电纺纤维结构的附着力及其抗拉强度的预测
46通过使用Box–Behnken设计将生物活性玻璃颗粒掺入明胶/聚(ε-己内酯)纳米纤维中来制造纳米复合材料垫
47Ca3(PO4)2沉淀的原位杂交PVA / Ca2O4Si纳米纤维抗菌伤口敷料的分层
48通过静电纺丝涂层制备用于人工组织的蛋白质支架
49基于聚(ε-己内酯)和聚(乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物)的纳米纤维支架的pH传感比较研究
50含谷氨酰胺的电纺纳米纤维的制备和表征
51结构聚(丙烯腈-乙酸乙烯酯)/氧化石墨烯的结构表征52基于电纺聚偏二氟乙烯纤维的耐用粘合剂
53静电纺丝—商业应用,挑战与机遇
54US20160274030A1成分和测量分析物的方法
55环氧乙烷,高压釜和紫外线杀菌对宠物电纺纤维表面形貌的影响
56使用静电纺丝技术在干胶应用中制造PVDF分层原纤维结构
57用于牙科应用的人工唾液中硅酸盐基45S5和13-93生物活性玻璃的体外矿化研究
58分层结构的电纺纳米纤维,用于改善雾气收集应用
59A对比研究脂肪酶固定在藻酸盐基复合电纺纳米纤维上的有效性和增强的稳定性
60wu定形非诺贝特的结晶和聚合物共混物电纺基体稳定在其wu定形形式的潜力
61基于智能手机的水中染料检测,以实现环境可持续性
62通过工艺参数为组织工程应用量身定制电纺纳米纤维的体系结构和本征结构
63聚(l-乳酸)/氧化石墨烯纳米纤维的神经再生理化特性
64药物的递送和抗HIV杀菌剂的开发
商用纳米纤维非织造布支持的用于正向渗透的65薄膜复合膜
66基于分层聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯电纺纤维的干胶
67具有抗菌功能的静电纺丝聚己内酯纤维膜的制备和表征
68超细纤维wu针静电纺丝的新进展:从学术界到工业生产
69具有高润湿性的热敏电纺膜
70Electrospun串珠分层纤维,用于雾气收集
表面增强拉曼散射平台上铝箔上的71维三维Au涂层电喷涂纳米结构BODIPY膜及其催化应用
72A高通量聚乙酸乙烯酯涂层电纺尼龙6
/ SiO2复合微滤膜,用于分离水包油乳液,具有改善的防污性能
73. 立柱长宽比对分层电纺纤维结构剪切粘合强度的影响
74通过碱解和氯化生产的抗菌聚丙烯腈纳米纤维
75电纺前后等离子体处理对电纺PCL纳米纤维的影响以改善细胞相互作用
76使用电纺锅膜过滤果汁
77从小分子到材料的光敏材料的基础研究
78在带有外部平面电j的RF等离子反应器中通过等离子聚合对表面进行疏水涂层:合成,表征和生物相容性
79聚(ε-己内酯)-聚多巴胺涂层纳米纤维和聚(ε-己内酯)-碳纳米管复合支架的力学性能和疲劳分析
80三层强力霉素-胶原蛋白纳米纤维伤口敷料的评估
81各向异性微纤维支架增强了诱导多能干细胞衍生的心肌细胞的组织和功能
82热响应性醋酸纤维-聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)核壳纤维,可控制地捕获和释放水分
83微纤维支架增强内皮分化和诱导的多能干细胞的组织
84大气压等离子体射流处理聚ε-己内酯聚合物溶液以改善静电纺丝
85甘蔗渣衍生的纤维素增强了组织工程用聚丙交酯和聚二恶烷酮电纺支架的性能
86用于集水应用的热敏电纺纤维
87介电阻挡放电(DBD)处理对壳聚糖/聚环氧乙烷纳米纤维及其细胞相互作用的影响
88等离子体处理对纳米纤维支架的表面化学,润湿性和细胞相互作用的影响
89Electrospinning(静电纺丝):一种通用的加工技术,用于生产生物医学和组织工程应用的纳米纤维材料
90纳米纤维的溶液电纺
91体外培养的细小乙烯基荧光菌确定制造结构的控制权
92用于释放阿霉素的静电纺丝聚氨酯纳米纤维垫的制备
93电纺鱼肌浆蛋白基纳米纤维的生产与表征
94.用于骨组织工程的聚(ε-己内酯)/磷酸三钙/六方氮化硼复合材料的新型纤维结构的生产
95提高纳米纤维产量-追求的进展,机制,挑战和原因
96Electrospun Janus膜可实现高效且可切换的油水分离
97镁合金防腐涂层-电纺超疏水聚苯乙烯/ SiO2复合纤维
98A两种不同集电器的电纺丝工艺比较研究-采集方法对纳米纤维直径的影响
99A单针和同轴电纺淀粉样蛋白纳米纤维研究亲水性药物释放行为的比较研究
激光等离子体实验中使用的低密度多孔材料的100A评述
101通过掺混或物理吸附法掺入环丙沙星的PLGA电纺支架的抗菌性能
102用于骨组织工程的含生物活性玻璃/羟基磷灰石的电纺聚(ε-己内酯)复合纳米纤维
具有高性能的103Core–Shell混合纳米线,能够实现快速的离子导电,可用于高性能复合聚合物电解质
104用于阴道内释放纳米药物的pH响应聚氨酯膜的设计和开发
105甲基泼尼松龙负载缓释纳米纤维的研制与表征
106通过电纺技术开发碳纳米纤维纱
107热处理条件对静电纺丝制备硼酸镁纤维的影响
108聚乙烯醇(PVA)/壳聚糖(CS)的混合比对电纺纳米纤维的形态,光学和热性能的影响
109温度,粘度和表面张力对改性3D打印机产生的明胶结构的影响
110聚甲基倍半硅氧烷浓度对电喷雾颗粒形貌的影响
111用于膜制造的静电纺丝-策略和应用
112静电纺制三乙酰基-β-环糊精(TA-β-CD)功能化的低密度聚乙烯,以大程度地减少硫味挥发性化合物
113围绕压印丙烯酸酯微球编织的电纺聚苯乙烯纤维,作为对羟基苯甲酸酯衍生物的吸附剂
114吲哚菁绿在聚乳酸纳米纤维中的封装,用作生物医学诊断中的纳米探针
115电纺聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯支架的制备:表征及其在体外细胞增殖中的潜力
116用可溶性淀粉包覆银纳米粒子制备抗菌聚乙烯醇纳米复合材料垫
117通过大气压等离子射流处理组织工程用电纺溶液制造PEOT / PBT纳米纤维
118用于膜蒸馏的高疏水性电纺还原氧化石墨烯/聚(偏二氟乙烯-六氟丙烯共聚物)膜
119用电喷雾微滴进行界面聚合-形成可控的超薄聚酰胺膜
120研究增强型电纺PLA纳米纤维的有机溶液中的等离子体诱导化学
121基于Levan的纤维支架通过同轴和单针技术进行电纺,用于组织工程
122微纳米原纤维聚己内酯支架作为可翻译的骨传导移植物,用于治疗wu感染的肌肉骨骼缺陷
123通过冷大气等离子体排列,抗菌活性和生物相容性对电纺PVA / PAA支架进行改性
124电纺聚乳酸和微晶纤维素的形态和力学特性
125基于明胶的非纤维弹性促进上皮组织形成
126PA6纳米纤维的生产:旋转喷射纺丝与静电纺丝的比较
127专利-US20180142379A1-含氟聚合物的静电纺丝
128专利-US20180215882A1-可溶胀和不可溶的纳米纤维及其在处理基本水性废水中的用途
129专利-US20180301690A1-金属氧化物纳米纤维电j和方法
130.聚乳酸溶液的130Plasma改性以产生高质量的静电纺PLA纳米纤维
129.聚乙烯醇复合纳米纤维的制备及固相聚乙烯醇的光催化降解132通过静电纺丝作为高效的析氢催化剂制备的聚合物和金属氧化物结构的纳米纤维复合材料
133含13-93生物活性玻璃的电纺聚ε-己内酯复合纳米纤维垫的制备和矿化
134载有盐霉素的纳米纤维用于胶质母细胞瘤治疗。
135.纳米尺寸石墨烯涂层及电喷法纺粘wu纺布表面的表征136超疏水性EVA共聚物纤维-化学成分对润湿性和光物理性质的影响
137还原的掺杂氧化石墨烯的P(AN-VAc)纳米纤维毡/ PP纺粘多层纳米复合材料的电磁屏蔽效能研究
138通过静电纺丝将酸樱桃(Prunus
cerasus L.)浓缩物单轴和同轴包封及其体外生物可及性
139电纺聚乙烯纳米纤维的热导率
140细菌触发的基于核壳聚羟基链烷酸酯(PHA)的纳米纤维释放出有效的杀菌剂,用于伤口包扎应用
141运动学研究与研究纳米技术
142使用纳米纤维基电j检测有机分子
143使用受控工作参数进行电纺的wu规和高度对齐的PCL纤维的大范围直径刻度
144A对PCL薄膜和纳米纤维进行生产前和生产后等离子体处理以改善细胞-材料相互作用的比较研究
145基于聚己内酯/聚(琥珀酸乙烯酯)的按需释放生物杀灭剂的细菌响应性单核和壳核纳米纤维膜。
146在大气压下沉积在聚(ε-己内酯)纳米纤维网上的环丙胺基等离子体聚合物的生物相容性
147生物启发的支架诱导神经组织再生
148由共电纺丝胶原蛋白和PLLCL组成的仿生混合支架用于3D细胞培养
149基于TiO2纳米纤维的半导体湿度传感器的开发-吸附动力学和DFT计算
150硅藻壳结合PHBV / PCL-普鲁兰共电纺丝支架,用于骨组织工程
151双有效的核壳电纺支架-促进成骨细胞成熟并降低细菌活性
152灭菌过程中紫外线照射时间对纳米纤维伤口敷料性能的影响
153 CeO2纳米纤维负载的贵金属(Pt,Pd和Ru)催化剂用于CO氧化的电子显微镜研究
154静电纺丝和电纺纳米纤维-方法,材料和应用
155静电纺丝-设置和步骤
156离散纳米粒子的电喷雾沉积-脉冲场电喷雾的研究和分析应用
157纳米和微米直径的聚酯电纺纤维,负载抗氧化剂,可作为伤口敷料或组织工程支架
158聚己内酯(PCL)微粒中包裹的褪黑激素作为有前景的移植材料
159在Si3N4和Si3N4 / MWCNT陶瓷复合材料上检查新型电喷涂生物羟基磷灰石涂层
160使用高通量ACwu针wu集电纺丝技术制造具有纳米纤维包膜的双功能复合纱
161种柔性S / DPAN / KB纳米纤维复合材料,用作Li-S电池的wu粘合剂阴j
162从硼氢化钠衍生的化合物制氢-电纺纳米晶体Co3O4催化剂的制备及其活性
163改进了静电纺丝在氨硼烷甲醇分解制氢中生产的金属氧化物催化剂的催化性能
164改良的聚二恶烷酮骨架的多细胞反应,仿生矿化,血管生成和异物反应降低,用于骨骼组织再生。
165通过等离子体表面改性改善电纺聚丙烯腈纤维中碳纳米管的分散性
166铁修饰的蒙脱土/聚己内酯纳米纤维膜对Hg(II)吸附的动力学和等温线研究
167用于伤口愈合的电纺纳米纤维的新进展
168脂酶反应性电纺丝法治疗伤口敷料,用于伤口感染的同时识别和治疗
169wu针电纺
170. 基于聚(ε-己内酯)/槲皮素共混物和仿生细菌S层涂层的新型可控释的可生物降解和防污系统
171关于PHBV / PCL和PHBV / PLGA电纺垫的详细机械响应研究
172专利-US10197498B2-用于分析物测量的成分和方法
173专利-US10211449B2-电池电j和方法
174由聚己内酯和氧化再生纤维素组成的具有防粘层的聚丙烯复合疝气网
175在环境条件下通过溶液静电纺丝制成的聚丙烯超细纤维
176用于生物医学的电纺聚乳酸/海藻酸钠/橙色牡蛎壳复合纳米纤维的制备与表征
177通过单/多功能GO制备静电纺丝PCL基支架
178助剂和溶液性质对通过锌轴电喷雾处理获得的纳米粒子的形态性质的影响。
179流变学对由果胶和聚环氧乙烷共混物形成纳米纤维的作用
180电纺PCL纤维尺寸,取向和等离子体改性的表面化学对干细胞行为的协同效应
181电纺制锆酸钙纳米纤维的合成与表征
182具有固定的热稳定性,pH稳定性和可重复使用性的静电纺丝PVA / Zn2 +金属复合纳米纤维的合成和表征
183对位芳纶纳米纤维的合成与力学性能
184神经引导导管在镁合金中的应用
163. 电感耦合等离子体(ICP)聚合法对聚己内酯(PCL)纳米纤维进行硫醇化-物理,化学和生物学性质
186用于生物医学应用的电纺纳米纤维
187使用静电纺丝将分隔器层压到电j上
188 Y2O3-和MgO稳定的氧化锆纳米纤维的静电纺丝及热处理过程中演化相组成和形貌的表征
189使用电纺PVDF纳米纤维应变传感器测量线中的冲击特性
190在等离子体处理过的有机溶剂中形成的自由基和离子:合理研究增强聚己内酯电纺性的机理研究
191大气压等离子体射流处理的聚己内酯聚合物溶液的老化对静电纺丝性能的影响
192负载利奈唑胺的PLGA纳米纤维的静电纺丝:溶剂对其可纺性,药物递送,机械性能和抗菌活性的影响
193用于伤口愈合监测的光致变色复合纳米纤维垫
194电纺SiBNC纳米纤维的合成和形貌化 |






